Figure 1. The predominant otopathogen to cause AOM when multiple otopathogens were simultaneously present in the NP.
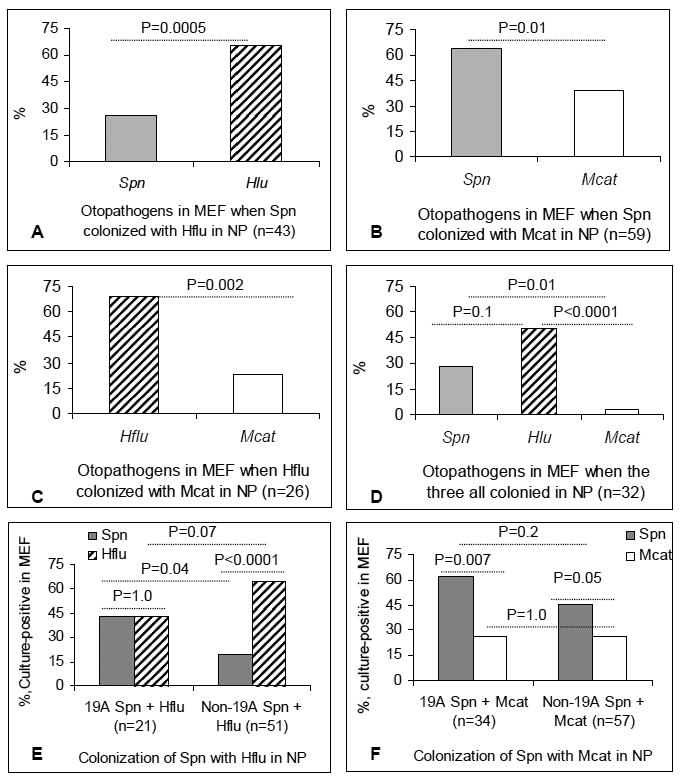
When multiple otopathogens were simultaneously present in the NP at the time of AOM the culture-positive rate in MEF was compared using logistic regression with repeated measures and Fisher's exact test. The percentage of each otopathogen causing AOM when co-colonization occurred involving, A, Spn with Hflu; B, Spn with Mcat; C, Hflu with Mcat; D, all three otopathogens; E, 19A or non-19A strains of Spn with Hflu; B, 19A or non-19A strains of Spn with Mcat. NP: Nasopharynx; MEF: middle ear fluid; Spn, S. pneumonia; Hflu: H. influenzae; Mcat: M.catarrhalis.
