Figure 6.
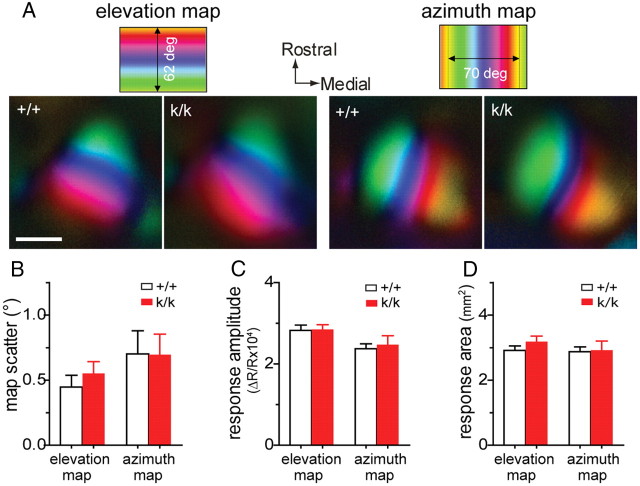
Basal response properties of the visual cortex in Bdnfklox/klox mice are normal. A, Examples of topographic maps of the visual cortex in response to the horizontal stripe moving vertically (left, elevation map) and to the vertical bar moving horizontally (right, azimuth map) on the monitor, recorded using intrinsic signal imaging. The color codes on top represent positions of different elevation lines (left) or azimuth line (right) at which specific location of the visual cortex is maximally responsive to the moving stripe. Scale bar, 1 mm. B, Map scatter. To assess the quality of the map, we computed the map scatter by calculating the differences between the phase values of the individual pixels within the visual area to those of their near neighbors. These phase differences would be very small if the maps are “high quality” because of the smooth progression of phases. C, Peak response amplitude presented as fractional change in reflection. D, Response area was calculated by selecting the pixels with the threshold of 30% of the peak amplitude. Error bars represent SEM. N = 4 +/+ mice and 5 k/k mice. There was no significant difference between +/+ and k/k mice (Student's t test).