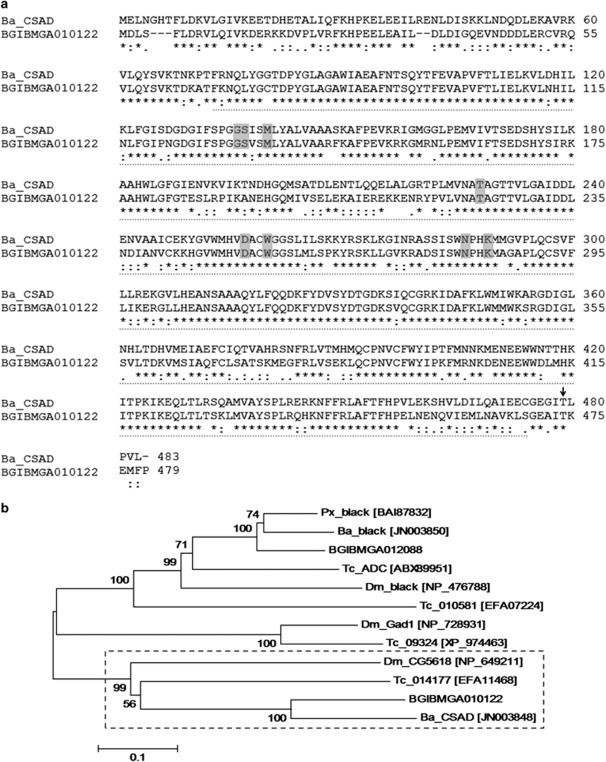
Figure 3.
Sequence annotation and phylogenetic analysis of Ba_CSAD. (a) Alignment of the predicted protein sequences of Ba_CSAD (483 amino acids) and its silkworm ortholog BGIBMGA010122 (479 amino acids). Numbers on the right show amino acid sequence position; sequence identities are marked with (*), conserved substitutions with (:) and semi-conserved substitutions with (.) (cf. MUSCLE, see Materials and methods). Dashed line indicates the PLP-dependent DOPA decarboxylase domain, gray boxes indicate pyridoxal 5′-phosphate-binding residues and the catalytic lysine (cf. NCBI Conserved Domains Search; see Materials and methods), and the arrow indicates the threonine, which is substituted by lysine in the mutant allele. (b) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree of Ba_CSAD and related insect proteins based on their amino acid sequences (with corresponding GenBank accession numbers), with bootstrap values for 1000 replications. Ba_CSAD, B. mori BGIBMGA010122, T. castaneum 014177 and D. melanogaster CG5618 form a separate clade, indicated with the dashed square. The scale bar indicates the evolutionary distance between the groups.