Figure 2.
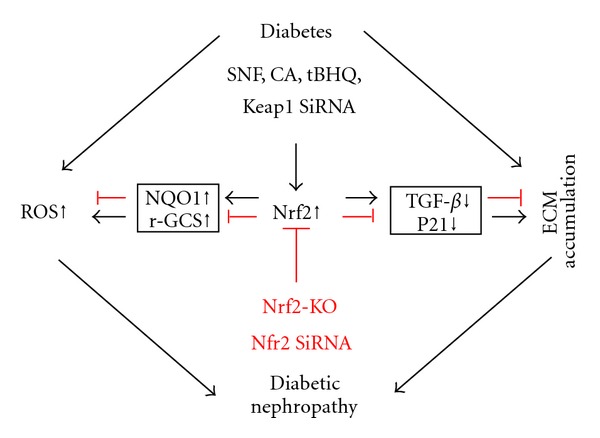
The protection by Nrf2 activation from diabetic nephropathy. Two main pathogenic factors leading to diabetic nephropathy in diabetic patients are increased ROS/RNS and extracellular matrix (ECM) accumulation. Activation of Nrf2 by SNF, CA, tBHQ, and Keap1 SiRNA or activation of Nrf2's downstream targets genes such as NQO1 and r-GCS plays an important role in preventing ROS/RNS-induced damage. At the same time, the expression of TGF-β and P21 was inhibited, leading to a prevention of ECM accumulation. Inhibition of Nrf2 in Nrf2-KO animals or by Nfr2 siRNA resulted in an enhancing diabetic effects. This illustration was made mainly based on a published study [22].
