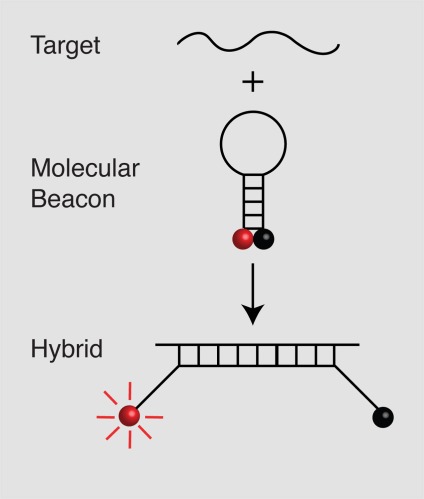
Figure 1. Principle of operation of molecular beacons.
In the free probes, a fluorophore attached at one of the molecule (red ball) is held close to a quencher (black ball) attached at the other end of the molecule, so that the probe is not fluorescent. The interaction of the sequence in the loop with the target separates the fluorophore and quencher and causes the fluorophore to become fluorescent.