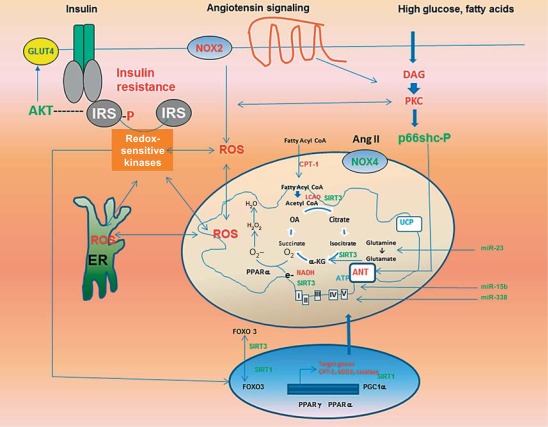
Fig. 1.
Sources and consequences of mitochondrial oxidative stress and its relationship to insulin resistance in the CRS. ROS-induced ROS release results from several pathways, including hyperglycemia and lipid-induced activation of PKC, Ang II-mediated activation of cytosolic (NOX2) and mitochondrial (NOX) NADPH oxidase, activation of p66shc, ER stress, and dysregulation of nuclear and mitochondrial transcriptional response. The activation of redox-sensitive kinases induces insulin resistance through increased phosphorylation of serine residues in IRS proteins, which in turn suppresses insulin metabolic signaling.