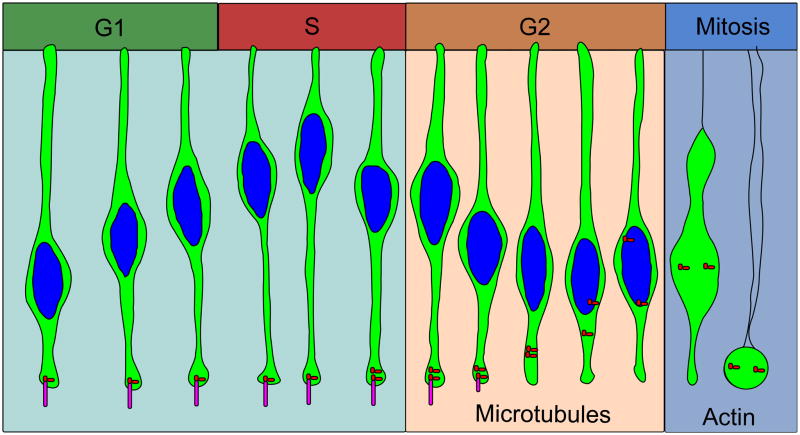
Figure 4. Proposed model of INM.
Nuclei are moved by actin contraction and along microtubules. Short nuclear movements may be accomplished by actin alone. Longer nuclear movements may require microtubules. Nuclei move basally during G1 phase, reaching a peak distance during S-phase. Nuclei begin moving apically along microtubules using the dynein motor protein during G2 phase. Tpx2 initiates apical nuclear migration at G2 phase. After cilia are lost, centrosomes can move to the nucleus during late G2 to initiate nuclear envelope breakdown and apical rounding, dependent on actin. Cytoplasm of the cells are shown in green, and nuclei are shown in blue. Centrosomes are red dots and cilia are magenta.