Figure 2.
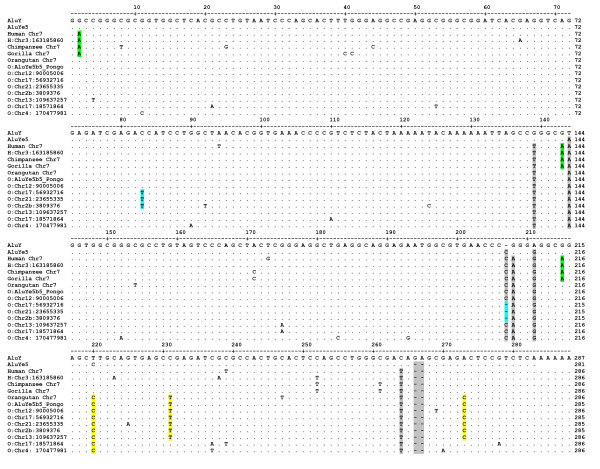
Alu Sequence alignment. The consensus sequence for the ancestral AluY subfamily is shown at the top. The dots represent the same nucleotide as AluY. Deletions are shown as dashes and mutations are shown as the corrected base. The chromosome 7 locus has a number of mutations different from AluY that are shared by all investigated species (highlighted in gray) and are all located in the right monomer of the element following the middle A-rich region. Post-insertion, the chromosome 7 locus in the orangutan (labeled Orangutan Chr7) independently acquired sequential diagnostic mutations (highlighted in yellow) shared by all polymorphic loci of the young AluYe5b5_Pongo subfamily in orangutans (starting with O:Chr). At some point, one of the AluYe5b5_Pongo members subsequently acquired one substitution and one deletion (highlighted in aqua) and has propagated as a daughter subfamily. Following the divergence of orangutan and the lineage leading to humans, the chromosome 7 locus acquired three substitutions (highlighted in green) shared in gorilla, chimpanzee and human. There is one human-specific Alu insertion, H: Chr3, which shares these three variants.