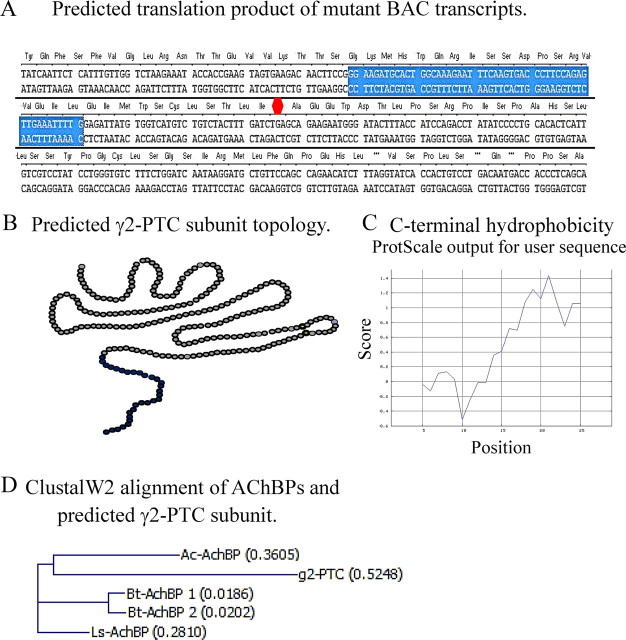
Figure 2.
The mutant BAC transcript was predicted to encode a truncated protein containing most of the γ2 subunit N terminus and a novel hydrophobic C-terminal tail translated from the retained intron 6 fragment and the exon 7 frameshift product. A, The predicted sequence of the C-terminal tail of the GABRG2(IVS6+2T→G) BAC transcript (γ2-PTC subunit) is shown. The blue background shows the retained 53 bp intron 6 fragment, and the red octagon shows the position of the PTC in exon 7. Sequences of both DNA strands are shown. The predicted amino acids are shown in blue above the DNA sequences. B, The predicted membrane topology of the γ2-PTC subunit is shown. The gray circles represent the wild-type γ2 subunit N terminus 217 aa peptide. The dark blue circles represent the 29 aa novel C terminus translated from retained intron 6 and exon 7 frameshift product. C, The hydrophobicity of the novel C-terminal tail translated from retained intron 6 and exon 7 frameshift product was determined based on an amino acid scale (Abraham and Leo, 1987). The average hydrophobicities of five adjacent amino acids (y-axis) are plotted against the amino acid positions in the peptide (x-axis). D, Peptide sequence alignment by ClustalW2 showing the γ2-PTC subunit is homologous to AChBP identified from different species. Ac-AChBP, Aplysia californica; Bt-AChBP, Bulinus truncatusi; Ls-AChBP, Lymnaea stagnalis.