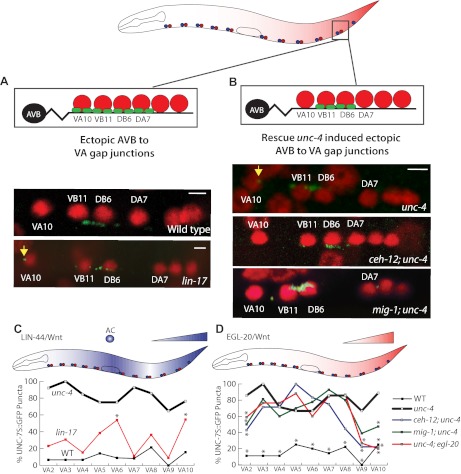
Fig. 6.
Opposing Wnt pathways regulate the specificity of gap junction inputs to VA motor neurons. (A) AVB gap junctions (green) with the cell soma of VB and DB motor neurons (red). Mutants of lin-17 (A) and unc-4 (B) show ectopic AVB to VA gap junctions (yellow arrows). (B) AVB gap junctions with posterior VAs depend on EGL-20. Mutations in ceh-12 and mig-1 suppress ectopic AVB gap junctions with VA10 in unc-4(e120) mutants. (C) lin-17 mutants display ectopic gap junctions near known sources of LIN-44 in the anchor cell (AC) (VA6) and tail region (VA10). (D) ceh-12, mig-1 and egl-20(n585) mutants suppress ectopic AVB gap junctions with posterior VAs in unc-4(e120) mutants and with VA2. *P<0.05 versus WT (C) or unc-4 (D). n≥10 for each neuron.