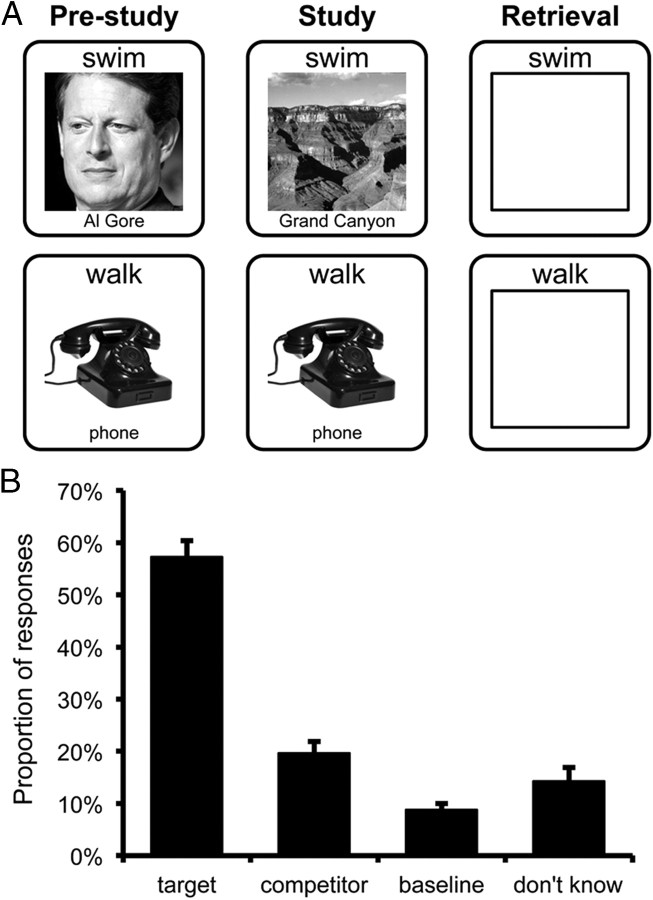
Figure 1.
A, Task diagram. During pre-study, subjects encoded initial word–image pairings. Images were drawn from one of three categories: faces, objects, or scenes. All pairings were encoded twice during pre-study. During study, all words were presented again and were either paired with a new image (change trials) or the same image as pre-study (repeat trials). At retrieval, subjects were presented with words and attempted to retrieve the most recent (or only) image paired with that word. Subjects responded by indicating the category of the image (face, object, scene) or by responding “don't know” via button press. B, Behavioral performance at retrieval for change trials where the original and newer images were from different categories (between-category change trials). Subjects were most likely to indicate the category of the newer (target) image, but were more likely to indicate the category of the older (competitor) image than a category never paired with that word (baseline). Error bars reflect standard error of the mean.