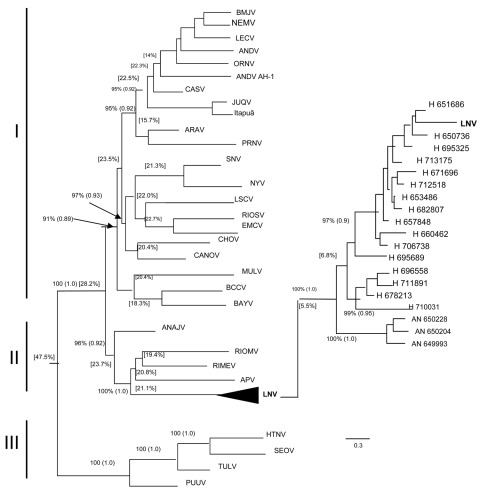
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic comparison of the partial nucleotide sequences of nucleoprotein (N) gene of the small (S) RNA segment of different hantavirus strains from the Old World and New World by using the maximum-likelihood method and Bayesian analysis, with detail of the phylogenetic relationship between LNV strains isolated from humans and rodents in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Bootstrap and Bayesian values (within parentheses) are shown for each respective knot. The arrows indicate the exact position of the values. Numbers within brackets correspond to the divergence between groups. Scale bar indicates 30% divergence of nucleotide sequences. APV, Alto Paraguay; ANAJV, Anajatuba, ANDV, Andes; BMJV, Andes Bermejo, NEMV, Andes Neembuco, LECV, Andes Lechiguanas; ORNV, Andes Oran; ARAV, Araraquara; BAYV, Bayou; BCCV, Black Creek Canal; CANOV, Cano Delgadito; CASV, Castelo dos Sonhos; CHOV, Choclo; EMCV, El Moro Canyon; HTNV, Hantaan; JUQV; Juquitiba-Araucaria; LNV, Laguna Negra; LSCV, Limestone Canyon; MULV, Muleshoe; NYV, New York; PRNV, Pergamino; PUUV, Puumala; RIOMV, Rio Mamoré; RIMEV, Rio Mearim; RIOSV, Rio Segundo; SEOV, Seoul; SNV, Sin Nombre; TULV, Tula.