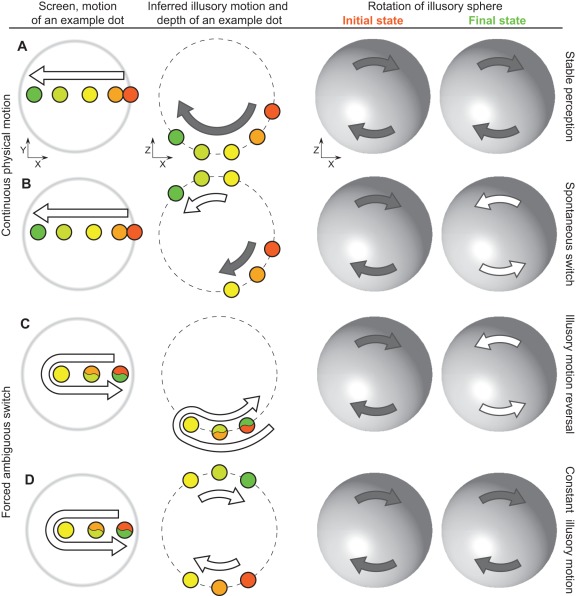
Figure 1. Structure-from-motion display and FAS paradigm.
Left column: a 2D motion of an example dot on the screen. Middle column: inferred illusory depth and illusory rotation of an example dot, as if viewed from above. Right column: initial and final direction of illusory rotation of an illusory sphere, as if viewed from above. Colour denotes position of the dot at various times: red – initial location, green – final location, intermediate hues – intermediate locations. A, B) Continuous motion (constant unperturbed planar flow motion, left column) may result (A) in a stable perception of illusory rotation or (B) in a spontaneous switch. In the latter case the illusory sphere reverses its direction of rotation (right column), while the individual dots alter both their illusory depth and direction of rotation (middle column). See also Video S1. C, D) Forced ambiguous switch (planar flow reverses its direction of motion, left column) may result (C) in an illusory motion reversal: illusory rotation of an illusory sphere is reversed (right column), illusory rotation of individual dots is also reversed, but depth remains constant (middle column). See also Video S2. D) Alternatively, illusory motion may remain constant (constant illusory motion outcome): here illusory rotation of both the illusory shape and of the individual dots remains constant, but the illusory depth of the dots is altered (middle and right columns). See also Video S3.