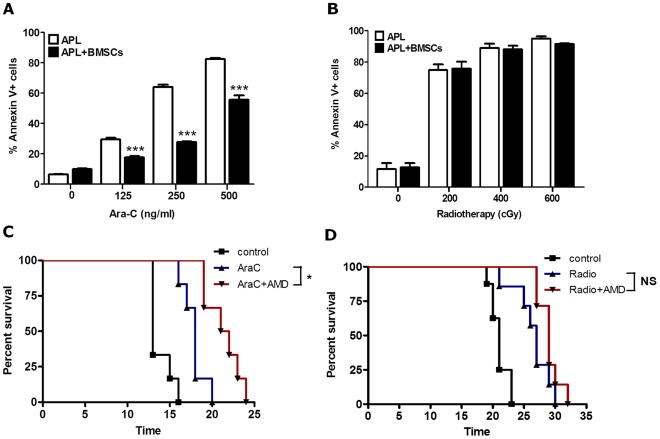
Figure 1. BM microenvironment modulates protection of APL cells to Ara-C induced apoptosis but not to radiation in vitro and in vivo.
(A) APL cells were cultured in absence or presence of M2-BMSCs for 2 hours before treatment with Ara-C (125, 250, 500 ng/ml) or vehicle alone (control). APL cell death was assessed by flow cytometry using a GR-1-APC mouse antibody and the annexin V-FITC apoptosis kit. (B) Cultures (as described 1A) were exposed to various radiation doses (200, 400 and 600 cGy) and allowed to recover for 24 before cell death was assessed as mentioned in (1A). (C) Kaplan Meier plot of overall survival of mice. Syngeneic B6129F1 recipient mice were intravenously injected with 106 APL cells. On day 12 post-APL injection, mice were left untreated (control; n = 6) or treated with AMD3100 alone (n = 7), Ara-C alone (n = 8), or the combination of AMD3100 and Ara-C (n = 8). Mice treated with chemotherapy received a single injection of Ara-C (500 mg/Kg) on days 12 and 13 post-APL injection. Mice treated with AMD3100 (5 mg/Kg) received subcutaneous injections 1 hour before and three hours after Ara-C treatment. (D) Kaplan Meier plot of overall survival of mice. Syngeneic B6129F1 recipient mice were intravenously injected with 106 APL cells. On day 12 post-APL injection, mice were left untreated (control; n = 6), exposed to radiation (350 cGy) (n = 8), or the combination of AMD3100 and radiation (n = 8). Mice treated with AMD3100 (5 mg/Kg) received a single subcutaneous injection 2 hours before radiation treatment. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. ***p<0.001 (APL + BMSCs versus APL). Overall survival of leukemic mice is not significantly prolonged when recipients are treated with the combination of AMD3100 and radiation versus radiation cohorts).