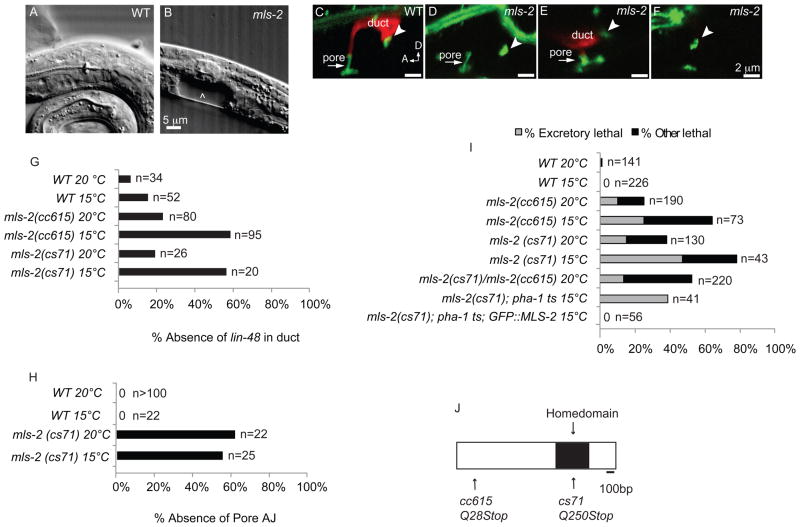
Figure 2. mls-2 mutants have incompletely penetrant and cold sensitive lethal excretory system defects.
(A) WT L1 stage larva. (B) mls-2(cs71) L1 stage larva showing fluid accumulation near duct and pore (arrowhead). (C-F) L1 worms with AJM-1::GFP junction marker and lin-48p::mcherry duct marker. Arrowhead, duct-canal cell intercellular junction. (C) WT larva with one duct and one pore. (D) mls-2 mutant with normal AJM-1::GFP but no lin-48 expression. (E) mls-2 mutant with normal lin-48 duct expression and collapsing pore. (F) mls-2 mutant with no lin-48 duct expression and no pore autocellular junction. (G,H) Quantification of marker loss phenotypes in mls-2 mutants. AJ, autocellular junction. (I) Rod-like (excretory) lethality shown as a fraction of total lethality. Other lethality scored as any worm that failed to reach L4 within 4 days. Note: GFP::MLS-2 rescue data scored by DIC microscopy looking for presence or absence of fluid cysts in L1s. Non-transgenic siblings were scored as controls. Complete genotype in this experiment was: mls-2(cs71); pha-1(e2123); Ex[GFP::MLS-2; pha-1(+)]. (J) Protein structure of MLS-2 showing the homeodomain and mutant alleles. cs71 changes a CAA codon (Q250) to TAA (stop).