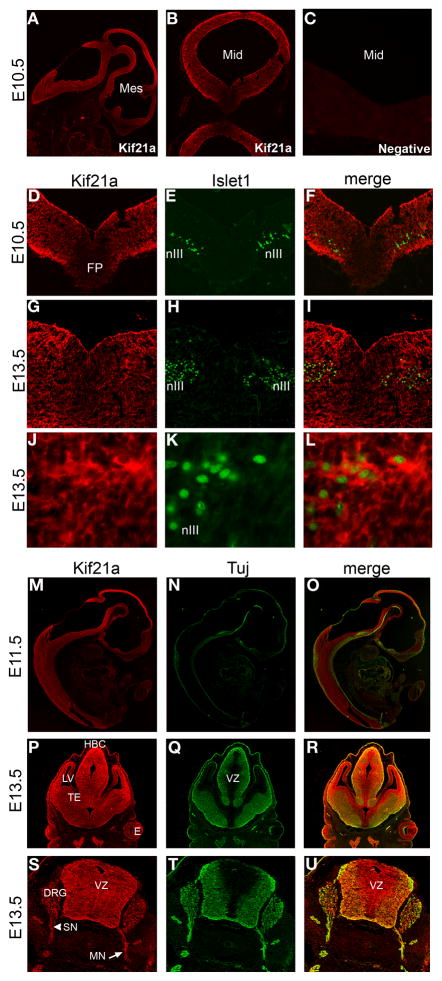
Figure 3. Spatial distribution of Kif21a in the developing mouse embryo.
(A–C) Sagittal and coronal sections of E10.5 mouse embryo immunostained with Kif21a (A,B) and 40X image of negative control without primary antibody (C). (D–L) Coronal sections through the midbrain of E10.5 (D–F) and E13.5 (G–L) mouse embryos co-immunostained with Kif21a and Islet1. Islet1 marks the nuclei of oculomotor neurons (nIII) seen at low power images in (D–I) and high power images 60X magnification in (J–L). (M–U) Cryosections of mouse embryos co-immunostained with Kif21a and Tuj1 antibodies. (M–O) Mid-sagittal sections through an E11.5 embryo. Kif21a protein is observed in a diffuse staining pattern throughout the developing CNS. (P–R) Coronal sections of E13.5 developing forebrain. Kif21A immunoreactivity is detected in both the ventricular and post mitotic mantle zones with only a few areas of negative staining. Kif21a is detected at higher levels in the regions of the habenular commissure and lateral ventricle. (S–U) Transverse sections through E13.5 spinal cord, highlighting expression in spinal motor and sensory axonal projections and dorsal root ganglia. All images are 10X magnification unless otherwise indicated. Abbreviations used are as follows: Mes = mesencephalon; Mid = midbrain; SC = spinal cord; FP = floor plate; nIII = oculomotor nucleus; HBC = habenular commissure; LV = lateral ventricle; TE = thalamic eminence; E = eye; VZ = ventricular zone; DRG = dorsal root ganglion; SN = DRG sensory nerve; MN = spinal motor nerve.