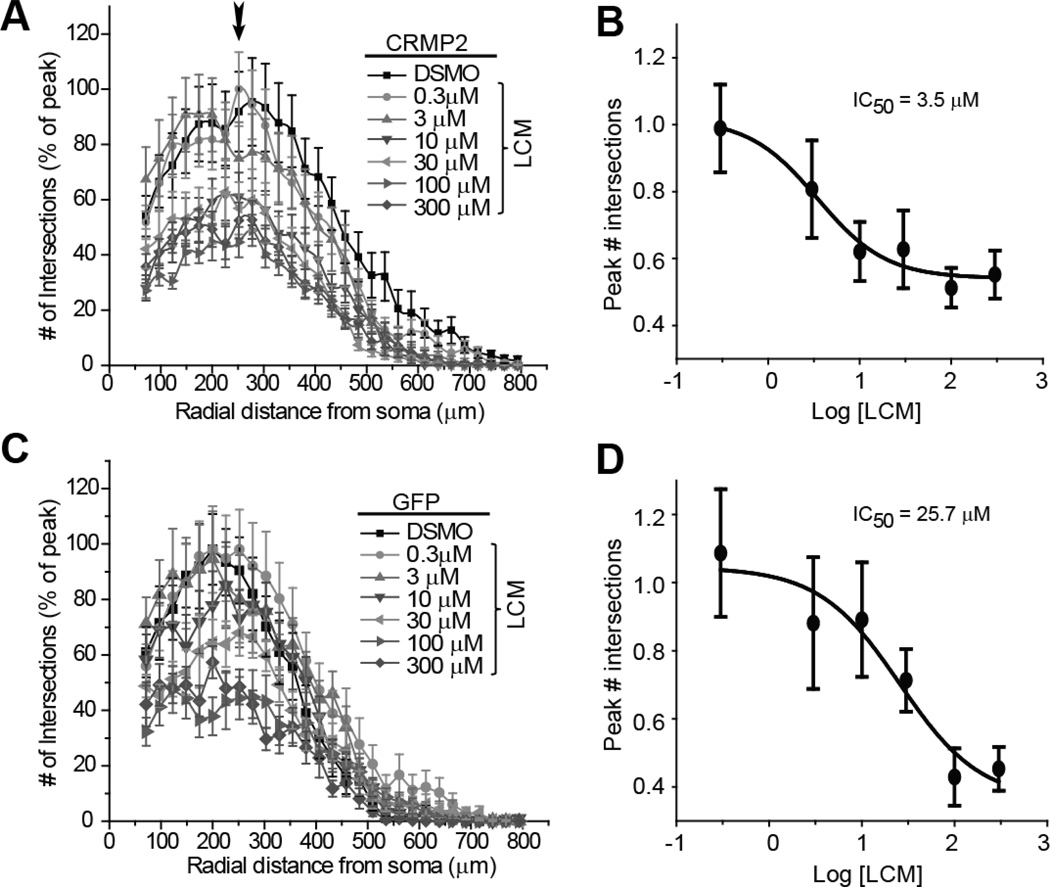
Figure 3. Lacosamide causes a dose-dependent reduction in neurite outgrowth of cortical neurons.
Sholl analysis of cortical neurons transfected with CRMP2-EGFP (A) or EGFP (C) and treated for 24 hr with 0.3 µM to 300 µM LCM or 0.01% DMSO (control). To allow direct comparison of the effect of LCM between CRMP2-EGFP and EGFP expressing cells, number of intersections was normalized to the maximum number of intersections in each experiment. Arrow in A denotes the peak number of intersections, which occurred at ~275 µm radial distance from the soma. Logarithmic dose-response plots of mean peak # of intersections for CRMP2-EGFP (B) and EGFP (D) transfected neurons. Average peak # of intersections, obtained from the Sholl analyses, were normalized to the average peak # of intersections in the vehicle (DMSO)-treated condition. The IC50 for inhibition of neurite complexity by LCM was determined by fitting the curve to a Sigmoidal dose response function (n= 15–25 cells for each condition from at least 3 separate culture wells).