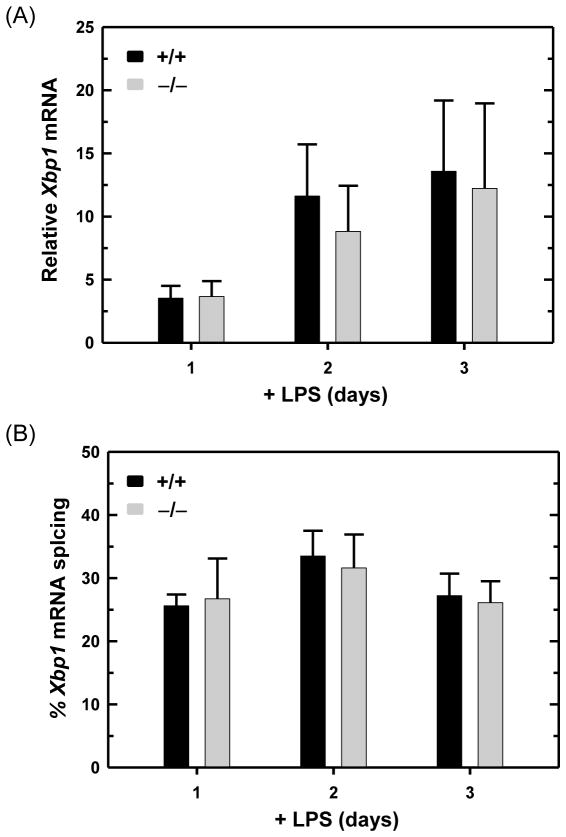
Fig. 7.
Expression and UPR-mediated splicing of Xbp1 mRNA in LPS-stimulated wild-type and ATF6α-deficient B cells. Splenic B cells were isolated from Atf6a+/+ and Atf6a−/− mice and cultured in the presence of LPS for the indicated intervals. (A) The level of total Xbp1 mRNA was assessed by qRTPCR. Data are plotted as the level of Xbp1 mRNA in LPS-stimulated cells relative to that in freshly isolated, resting cells (set at 1) (mean ± S.D., n = 3). (B) The percentage of Xbp1 transcripts modified by UPR-mediated splicing (mean ± S.D., n = 3) was determined by resolving RT-PCR products amplified from unspliced and spliced Xbp1 mRNA (237 and 211 nts, respectively) by gel electrophoresis followed by imaging and quantification.