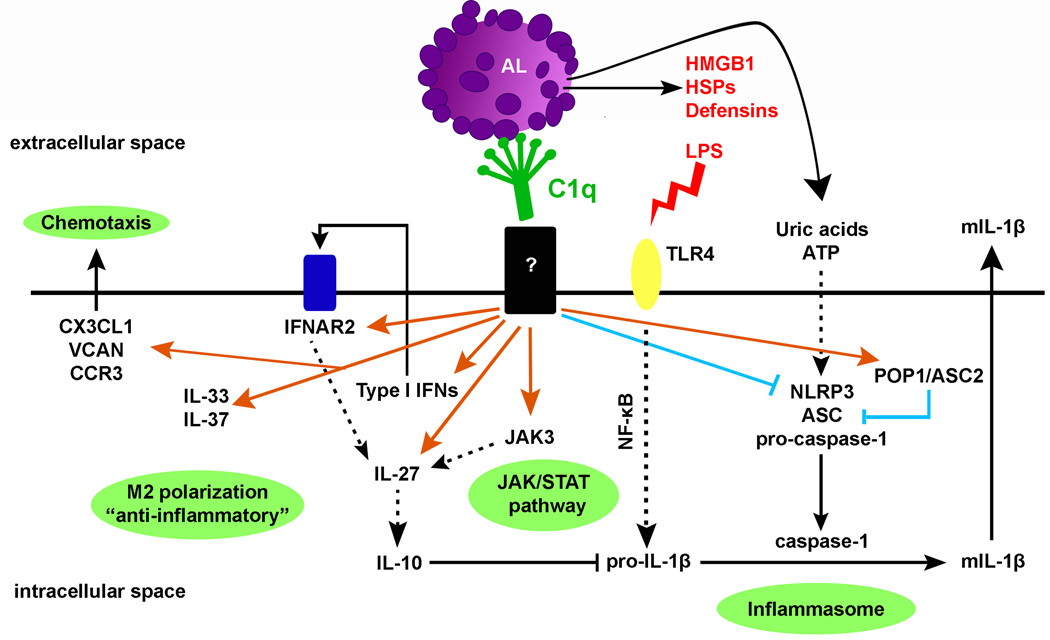
Figure 7. Main biological pathways modulated by C1q in HMDMs.
C1q increases the expression of type I IFNs and IL-27, known to act sequentially to stimulate expression of IL-10 (also up-regulated by C1q), IL-33, known to promote alternative activation of macrophages, IL-37, a potent natural suppressor of innate inflammatory responses and JAK3 that may be involved in IL-27 up-regulation. C1q also suppresses procaspase-1 and pro-IL-1β cleavage and subsequent mIL-1β release through possibly increase expression of negative regulators of inflammasome activity and indirectly (at later times) through increase IL-10 expression, which is known to decrease pro-IL-1β mRNA levels. C1q may thus prevent excessive and dysregulated inflammasome activation induced by the release of DAMPs (HMGB1, HSPs, ATP) from apoptotic cells during secondary necrosis that can activate TLR4 and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Orange arrows represent up-regulated genes and blue lines represent down-regulated genes by C1q.