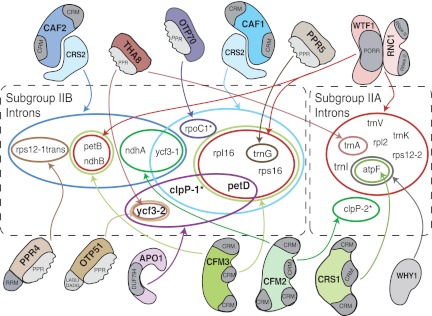
FIGURE 9.
Summary of nucleus-encoded proteins that promote the splicing of group II introns in angiosperm chloroplasts. Mutations in genes encoding the indicated proteins in maize (CAF1, CAF2, CRS1, CRS2, OTP51, PPR4, PPR5, RNC1, THA8, WHY1, WTF1) and/or Arabidopsis (CRS1, CAF1, CAF2, THA8, OTP51, OTP70, CFM2, CFM3) disrupt the splicing of the indicated introns. Where orthologous proteins have been analyzed, intron targets are conserved. All of the proteins analyzed in maize have been shown to coimmunoprecipitate with those introns whose splicing they promote. OTP51 has several minor targets (trnK, trnV, atpF, petB) not diagrammed (Falcon de Longevialle et al. 2008; Supplemental Fig. S2B). The MatK protein encoded in the trnK intron associates with all chloroplast subgroup IIA introns and is likely to be required for their splicing (Zoschke et al. 2010). This information is summarized (Jenkins et al. 1997; Vogel et al. 1999; Jenkins and Barkan 2001; Till et al. 2001; Ostheimer et al. 2003; Asakura and Barkan 2006, 2007; Schmitz-Linneweber et al. 2006; Watkins et al. 2007; Asakura et al. 2008; Beick et al. 2008; Falcon de Longevialle et al. 2008; Prikryl et al. 2008; Kroeger et al. 2009; Chateigner-Boutin et al. 2011; Watkins et al. 2011).