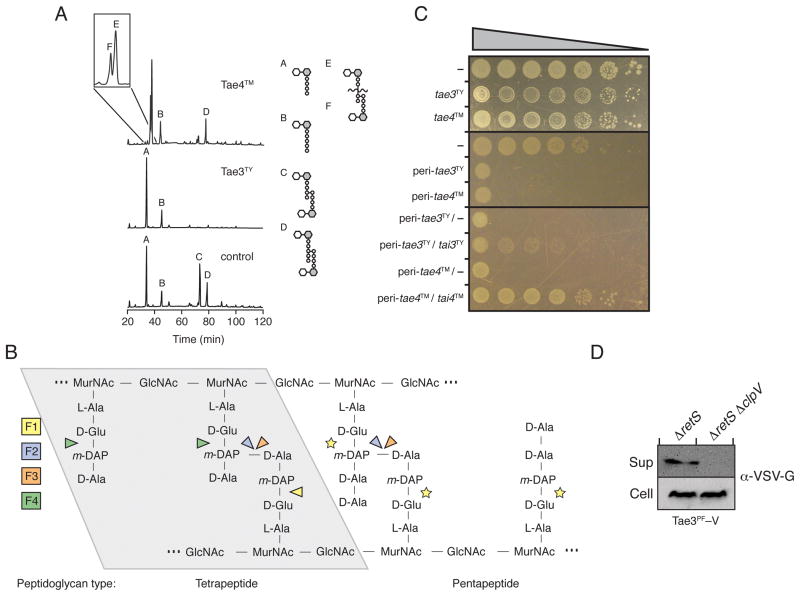
Figure 4. Representatives of Families 3 and 4 are T6S amidase EI pairs.
(A) Tae3TY and Tae4TM are peptidoglycan amidases with specificity for the m-DAP-D-alanine DD-bond and the γ-D-glutamyl-L-m-DAP bond, respectively. Partial HPLC chromatograms of sodium borohydride-reduced soluble E. coli peptidoglycan products resulting from digestion with Tae3TY or Tae4TM and subsequent cleavage with cellosyl. The control sample was digested with cellosyl alone.
(B) Simplified representation of Gram-negative peptidoglycan showing cleavage sites of effector families 1–4 (F1-4) based on HPLC data. Cleavage specificity on peptidoglycan with tetrapeptide (left) and pentapeptide (right) stems are depicted. Tse1 activity against pentapeptide-rich peptidoglycan has not been tested, as indicated by yellow stars. Abbreviations: GlcNAc, N-acetyl-glucosamine, MurNAc, N-acetyl-muramic acid.
(C) Tae3TY and Tae4TM are toxic in the periplasm and this toxicity is rescued specifically by cognate immunity proteins, Tai3TY and Tai4TM, respectively. Growth of E. coli harboring one (top panels) or two (bottom panel) vectors expressing the indicated genes. A dash indicates the empty vector. From left to right are increasing serial ten-fold dilutions. Expression data for this experiment are shown in Figure S2.
(D) Tae3PF is secreted in a T6SS-dependent manner. Western blot analysis of supernatant (Sup) and cell-associated (Cell) fractions of the indicated P. fluorescens strains expressing vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein (VSV-G) tagged Tae3PF (Tae3PF –V).