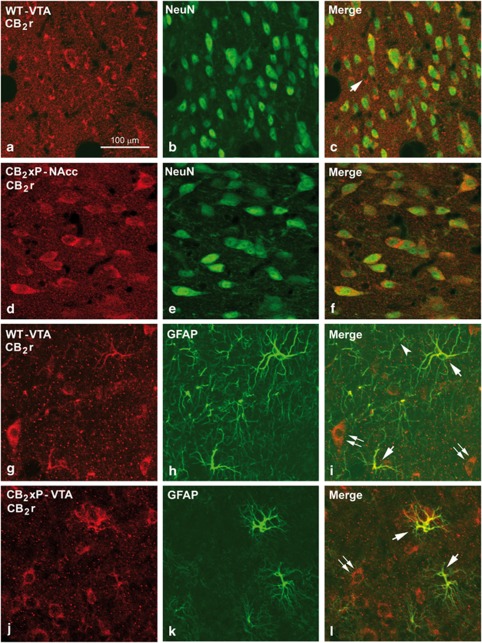
Figure 6.
Immunolabeling for CB2 receptors (CB2r) and neuronal nuclei (NeuN) in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and the nucleus accumbens (NAcc) and for CB2r and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the VTA of wild-type (WT) and CB2r overexpressing (CB2xP) mice. Confocal photomicrographs showing immunolabeling for CB2r (red cells in (a) and (d)) and NeuN (green cells in (b) and (e)) in the VTA of WT and the NAcc of CB2xP mice. Double labeling (yellow cells in (c) and (f)) both in the VTA and the NAcc indicates that most of the CB2r immunoreactive (i.r.) cells are neurons. A CB2r cell not labeled for NeuN is shown in (c) (arrow). (g–l) Immunolabeling for CB2r (red cells in (g) and (j)) and GFAP (green cells in (h) and (k)) in the VTA of WT and CB2xP mice. Double labeling (yellow cells in (i) and (l)) shows that most of the GFAP i.r. astrocytes are also immunolabeled for CB2r (arrows in (i) and (l)). GFAP i.r. astrocytes not CB2r i.r. can be rarely seen (arrow head). CB2r immunolabeled cells, most probably neurons, are showed in (i) and (l) (double arrow). Same scale for (b–l).