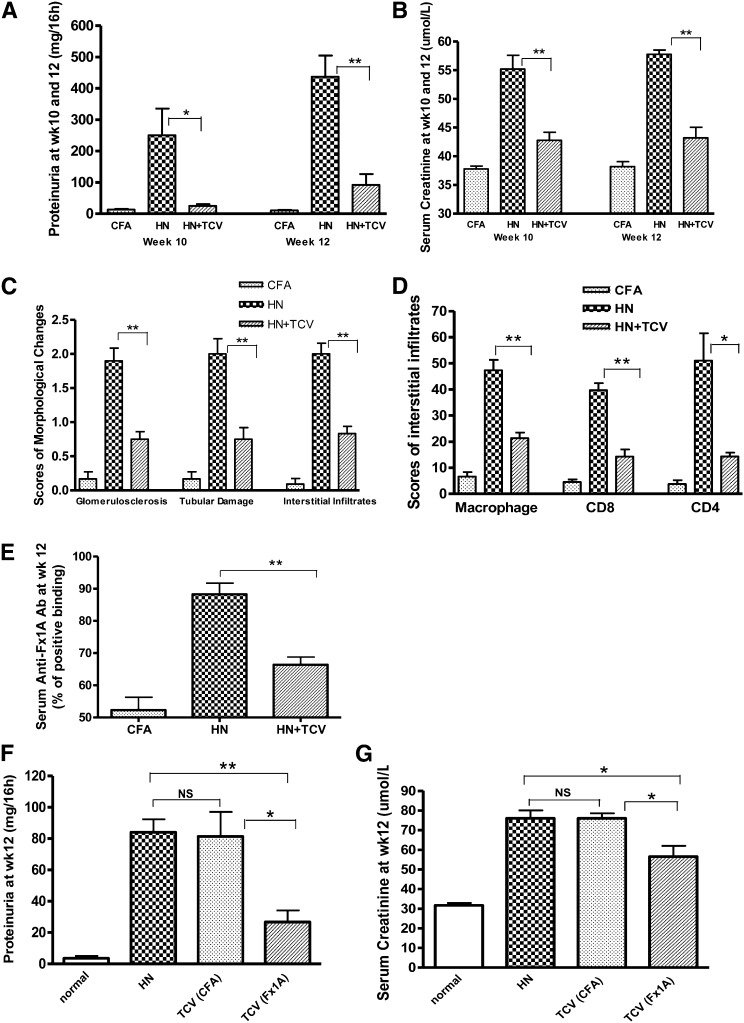
Figure 2.
TCV reduced proteinuria, inflammation, and protected renal function in HN, and the protection was induced by antigen-specific TCV. HN + TCV rats had significantly reduced (A) proteinuria excretion at weeks 10 and 12 and (B) serum creatinine compared with HN rats. (C) Semiquantitative scores of morphologic changes at week 12 showed significantly less damage in glomeruli and tubules and reduced interstitial monocyte infiltration in HN + TCV rats compared with HN rats. (D) Interstitial infiltration scores of macrophage and CD8+ and CD4+ cells on immunohistochemical sections showed reduced kidney infiltration in HN + TCV rats. (E) Comparison of Fx1A IgG responses in the three groups of rats; anti-Fx1A antibody levels expressed as percentage binding of known positive serum (anti-Fx1A titer; 1:200) measured by ELISA were significantly reduced by TCV in the course of HN. (F) Proteinuria and (G) serum creatinine were significantly reduced in Fx1A-primed TCV rats compared with CFA-primed TCV (n=6 for each group, mean ± SD). *P<0.05; **P<0.01.