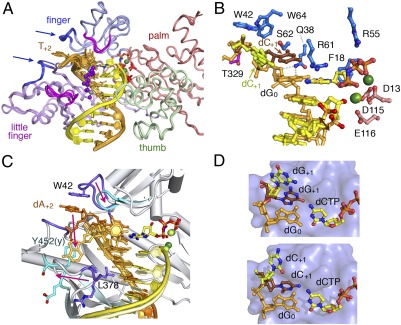
Fig. 2.
Structural features of hPol η ternary complexes. (A) Superposition of six hPol η–DNA complexes. The protein is shown as Cα traces, and the four domains are color-coded. The DNA template strand is drawn in orange and primer in yellow. Cisplatin is shown as purple and gray spheres. Mg2+ ions (green spheres), catalytic carboxylates (red sticks), and incoming nucleotides (yellow and multicolored sticks) are also shown. Two generally mobile loops are shown in blue and pointed out by arrows, and the two, whose movement is coupled with the presence of DNA lesions, are shown in magenta. (B) The active site of GG0b. The nucleotide downstream of the templating base (dC+1) has two conformations; so does the 3′ nucleotide of the primer strand. (C) Superposition of human (PDB ID code 3MR3) (25) and yeast Pol η (PDB ID code 3MFI) (26) complexed with CPD. The protein loops involved in template-strand binding, the DNA, and metal ions are shown in darker color in the human complex than in the yeast. Pink arrows indicate the changes from human to yeast. (D) Two conformations of the nucleotide downstream of the templating base. Upper is GG0a (dG+1), and Lower is GG0b (dC+1).