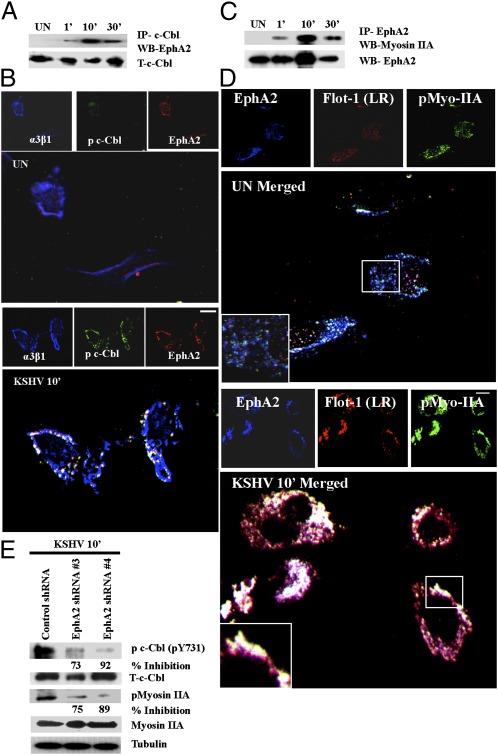
Fig. 4.
KSHV-recruited EphA2 induced the formation of a c-Cbl, integrin, and myosin internalization complex. (A) Serum-starved HMVEC-d cells were either left uninfected or KSHV infected for the indicated time points and immunoprecipitated with anti–c-Cbl antibody and analyzed for EphA2 by Western blot. (B) Serum-starved (8 h) HMVEC-d cells were either left uninfected (UN) or infected for 10 min with KSHV (10 DNA copies per cell), washed, and processed for immunofluorescence assay using goat anti-EphA2, mouse anti-α3β1, and rabbit anti–c-Cbl antibodies for 1 h at 37 °C. Subsequently, cells were stained with anti-mouse Alexa fluor 405, anti-goat Alexa fluor 594, and anti-rabbit Alexa fluor 488, respectively. Representative 2D deconvoluted images are shown. (Scale bar: 10 μm.) (C) Serum-starved HMVEC-d cells were either uninfected or KSHV infected for the indicated time points, immunoprecipitated with EphA2 antibody, and Western blotted for myosin IIA. The blot was stripped and reprobed for EphA2. (D) Serum-starved uninfected (UN) or KSHV-infected HMVEC-d cells were processed as in C and immunostained for EphA2, p-myosin IIA, and LR marker (Flotillin-1). Representative images are shown. The boxed region in the merged panel is enlarged and shown in the Inset. (Scale bar: 10 μm.) (E) Control or EphA2 shRNA-transduced HMVEC-d cells were subjected to Western blot analysis for the indicated phosphorylated (activated) signal molecules. The blots were stripped and reprobed for the respective total c-Cbl and myosin IIA with tubulin as a loading control. The levels of inhibition are indicated.