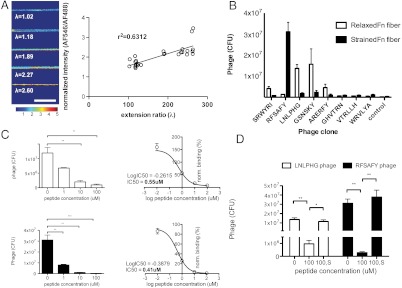
Fig. 2.
Isolation of specific phage clones targeting Fn fibers under varying strain. (A) Increased strain in Fn fibers correlates with unfolding of Fn type III domains. A thiol-reactive compound (AlexaFluor 546-maleimide) was used to detect the unmasking of the buried free cysteine residues in FnIII7 and FnIII15. Amount of free cysteine detected (unfolding of FnIII7 and/or FnIII15) correlated with Fn fiber strain. Images were acquired at 63×, shown is normalized intensity of AF546 channel divided by AF488 channel. (Scale bar: 20 μm.) (B) Binding of individual clones to Fn fibers under varying strain. Eight clones were individually assayed for their binding to Fn fibers. Each experiment used 1 × 1011 phage. Control phage was phage population after round three of panning. (C) Competitive inhibition of phage clones with soluble peptides at increasing concentrations. Two phage clones that show the greatest dynamic range in difference between binding relaxed (Upper, LNLPHG phage) and strained (Lower, RFSAFY phage) Fn fibers were characterized for their binding specificity. Each phage clone was coincubated with its corresponding displayed peptide at increasing concentrations. Data were fitted using a nonlinear log (inhibitor) vs. normalized response fit and IC50 values were calculated to 0.55 μM for LNLPHG phage, and 0.41 μM for RFSAFY phage. N > 3 for all samples, error bars are SEM. Statistics were performed using a one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest correction. (**, p < 0.01) (D) Scrambled soluble peptides do not inhibit binding of phage clone to Fn fibers. Phage clones displaying either the LNLPHG or RFSAFY peptide were incubated with its corresponding peptide or a scrambled peptide (HLNPGL or AYSRFF) at 100 μM in the presence of relaxed (λ = 0.93) or strained (λ = 2.64) Fn fibers, respectively. Incubation with 100 μM peptide that matched the phage-displayed peptide showed competitive inhibition (labeled “100”), whereas incubation with scrambled peptides did not (labeled “100, S”). N > 3 for all samples, error bars are SEM. Statistics were performed using a one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest correction (*, p < 0.05, ** p < 0.001).