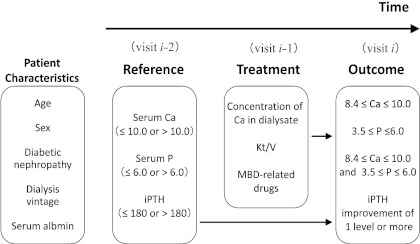
Figure 1.
Regression model used in the analyses of factors likely to affect the achievement of guideline-specified targets: The model assumes that laboratory values may cause changes in treatment, which may in turn modify later laboratory values. Patients' characteristics included age (<65 or ≥65 years), gender (male or female), diabetic nephropathy (no or yes), number of years of dialysis treatment (<10 or ≥10 years), and serum albumin (<3.5 or ≥3.5 g/dl). Reference values included phosphorus in serum at baseline (≤6.0 or >6.0 mg/dl), calcium in serum at baseline (≤10.0 or >10.0 mg/dl), and iPTH in serum at the reference visit (≤ 180 or >180 pg/ml). Treatments included calcium in dialysate (<3.0 or ≥3.0 mEq/L), Kt/V (<1.2, 1.2 to <1.6, or ≥1.6), an intravenous vitamin D receptor activator (none, oral VD alone, or intravenous VD), a phosphate binder (none, calcium-based phosphate binder alone, non-calcium-based phosphate binder alone, or both calcium-based and non-calcium-based phosphate binders), and cinacalcet (no or yes). Outcomes were defined in reference to the JSDT guidelines for calcium, for phosphorus, for both calcium and phosphorus, and for iPTH.