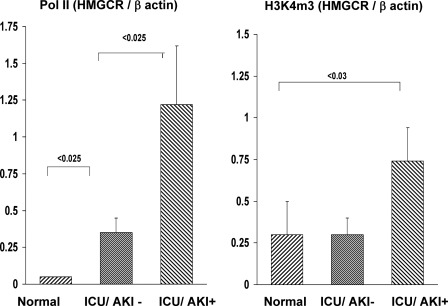
Figure 1.
Patients with AKI manifest increased levels of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) and of histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4m3) at exon 1 of HMG–CoA (HMGCR) gene in urine chromatin samples. Urine pellet samples from normal subjects, intensive care unit/acute kidney injury (ICU/AKI)+ patients, and ICU/AKI− patients were probed for Pol II and H3K4m3 at exon 1 of the HMGCR gene (ChIP assay; all results factored by amounts of Pol II and H3K4m3 at exon 1 of the house keeping gene β-actin). Increased Pol II levels were observed in both ICU cohorts, versus normal controls, but the levels were approximately fourfold greater in the AKI+ patients versus the AKI− controls. The AKI+ patients had a twofold increase in H3K4m3 levels at the HMGCR gene, whereas no increase was seen in the ICU/AKI− population. Thus, these data support the concept that AKI causes increased expression of the HMGCR gene. Values are presented as means ± 1 SEM.