Figure 2. Application of CONGA to an example pair of metabolic networks.
(A) In these two example networks, substrate (S) is utilized to produce biomass (BM) and some by-product (P). We refer to the two species as A and B, and the biomass- and product-producing reactions as  and
and  , respectively. (B) List of genes and reactions present or absent in each network. All shared reactions have orthologs present in both networks, except for the reaction associated with genes G23a and G23b, which are not orthologs. (C) A schematic view of the wildtype network behaviors in which flux through
, respectively. (B) List of genes and reactions present or absent in each network. All shared reactions have orthologs present in both networks, except for the reaction associated with genes G23a and G23b, which are not orthologs. (C) A schematic view of the wildtype network behaviors in which flux through 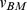 is maximized. (D) Gene deletion sets identified by CONGA for the stated CONGA objectives The first three objectives maximize
is maximized. (D) Gene deletion sets identified by CONGA for the stated CONGA objectives The first three objectives maximize 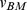 in Species B over Species A. The last objective maximizes
in Species B over Species A. The last objective maximizes  in Species A over Species B. The type of model difference (genetic, orthology, or metabolic) associated with each deletion set is also given. (E through H) Schematic views of the flux distributions associated with each gene deletion set in D. The optimal flux distributions in the example networks change as a result of the gene deletion sets in D. Differences in the optimal flux distributions are due to differences in the two networks.
in Species A over Species B. The type of model difference (genetic, orthology, or metabolic) associated with each deletion set is also given. (E through H) Schematic views of the flux distributions associated with each gene deletion set in D. The optimal flux distributions in the example networks change as a result of the gene deletion sets in D. Differences in the optimal flux distributions are due to differences in the two networks.

