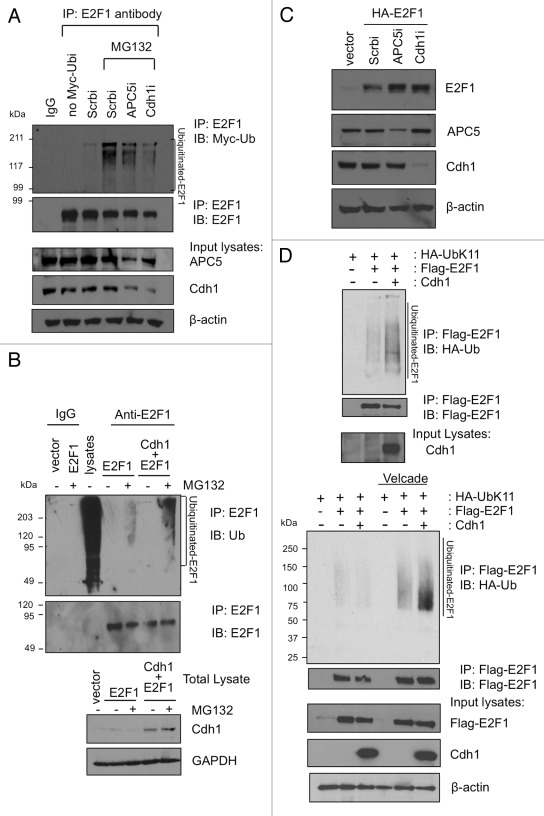
Figure 4. Cdh1 promotes K11-linkage specific ubiquitination of E2F1. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with Myc-ubiquitin along with vectors expressing siRNA for APC5, Cdh1 or a scrambled (Scrb) sequence control. The cells were left untreated or treated with MG132. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with normal mouse IgG or a monoclonal E2F1 antibody, followed by immunoblotting to detect ubiquitinated E2F1. An aliquot of total lysates were immunoblotted as indicated. (B) HEK293 cells were transfected either with a control empty vector, E2F1 alone, or E2F1 with Cdh1. The cells were left untreated or treated with MG132. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with normal mouse IgG or a monoclonal E2F1 antibody, followed by immunoblotting with ubiquitin antibody to detect ubiquitinated E2F1. “Lysates” lane is from total cellular lysates without immunoprecipitation and serves as a positive control for ubiquitin immunoblotting. Aliquots of each input lysate were also immunoblotted as indicated (below). (C) HEK293 cells were transfected with an empty vector or HA-E2F1 along with a vector expressing siRNA for APC5, Cdh1 or a scrambled (Scrb) sequence control. Two days later, cells were harvested and lysates were immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. (D) HA-Ub-K11-specific ubiquitin was overexpressed in HEK293T cells along with GFP-Cdh1 (or GFP vector control) and Flag-E2F1 as indicated in the presence (lower panel) or absence (upper panel) of proteasome inhibitor Velcade. Lysates were processed as described in Materials and Methods, and then immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag beads. The HA-Ub-K11-conjugated E2F1 were detected by HA immunoblotting.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.