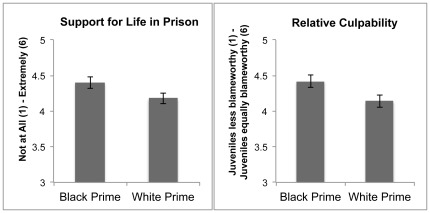
Figure 1. Effect of priming race on life without parole sentences and juveniles’ blameworthiness relative to adults.
Participants in the Black prime condition exhibited significantly greater support for life without parole sentences and viewed juveniles’ and adults’ culpability as significantly more similar than did participants in the White prime condition. Error bars represent standard errors of the means.