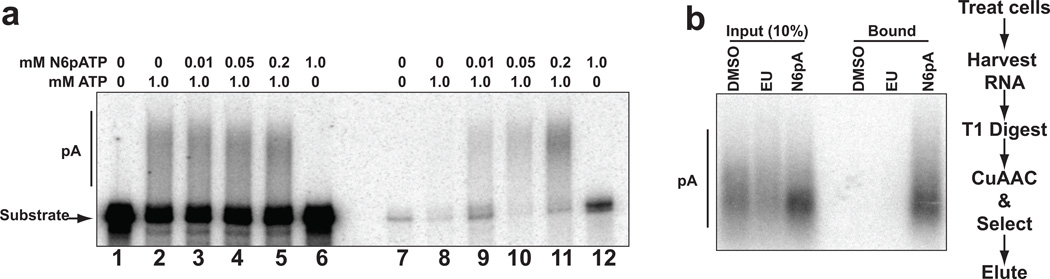
Figure 2.
N6pA is incorporated into poly(A) tails in vitro and in vivo. (a) In vitro polyadenylation assays with a 32P-labeled “pre-cleaved” substrate in HeLa nuclear extract.[4] The substrate is a 247-nt in vitro transcribed RNA derived from the 3′ end of PANΔ79 RNA[14] that contains the AAUAAA polyadenylation signal and terminates at the natural cleavage site. As a result, polyadenylation is uncoupled from the endonucleolytic cleavage step of 3′-end formation. The concentrations of N6pATP and ATP in the reaction are shown above each lane. Lanes 1–6 contain the products of the polyadenylation reaction (20% of the total reaction), while lanes 7–12 are the streptavidin-bound transcripts. (b) N6pA is incorporated into poly(A) tails in vivo. 10% of the RNase T1-treated RNA (Input) or 100% of the streptavidin-bound RNA was analyzed by northern blot using an oligo dT probe to detect poly(A) tails. The experimental flow is shown to the right.