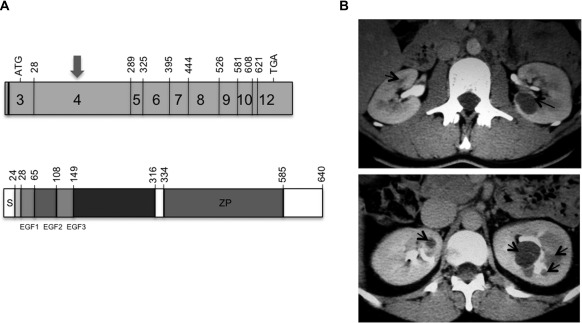
Figure 1.
Representation of UMOD gene and uromodulin protein and radiological features associated to UMOD or HNF1B mutation. (A) Schematic representation of UMOD gene and uromodulin protein. The shaded boxes represent the exons of UMOD gene encoding uromodulin (4,5). The number of the first codon of each exon is indicated. The codon that initiates traduction is in exon 3 (nucleotide 106). More than 80% of mutations are in exon 4 (arrow) (upper panel). Uromodulin protein is a 640-amino acid glycoprotein. The N-terminal region (mainly exon 4) contains three calcium-binding EGF domains followed by a highly conserved cysteine-rich sequence of 166 residues. The C-terminal region contains the zona pellucida (ZP) domain and a phosphatidylinositol anchor (lower panel) (4,5). (B) Injected computed tomography (CT) in two patients with UMOD and HNF1B mutation, respectively. CT in one patient with UMOD mutation showed bilateral corticomedullary cysts (5 mm on the right kidney and 20 mm on the left kidney) (arrows), and kidneys were of normal size (left panel). CT in one patient with HNF1B mutation showed normal kidney size with multiple bilateral medullary cysts (arrows), predominantly on the left kidney (right panel).