Table 4.
Relationship of head impact exposure metrics to postseason cognitive performancea
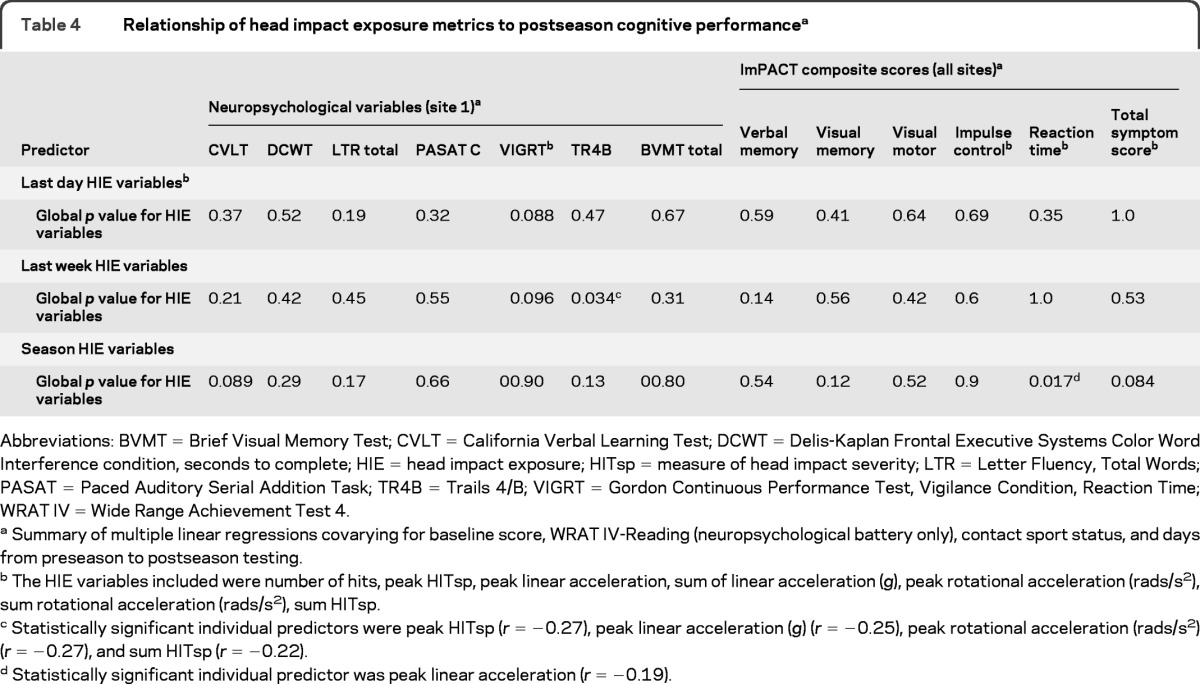
Abbreviations: BVMT = Brief Visual Memory Test; CVLT = California Verbal Learning Test; DCWT = Delis-Kaplan Frontal Executive Systems Color Word Interference condition, seconds to complete; HIE = head impact exposure; HITsp = measure of head impact severity; LTR = Letter Fluency, Total Words; PASAT = Paced Auditory Serial Addition Task; TR4B = Trails 4/B; VIGRT = Gordon Continuous Performance Test, Vigilance Condition, Reaction Time; WRAT IV = Wide Range Achievement Test 4.
Summary of multiple linear regressions covarying for baseline score, WRAT IV-Reading (neuropsychological battery only), contact sport status, and days from preseason to postseason testing.
The HIE variables included were number of hits, peak HITsp, peak linear acceleration, sum of linear acceleration (g), peak rotational acceleration (rads/s2), sum rotational acceleration (rads/s2), sum HITsp.
Statistically significant individual predictors were peak HITsp (r = −0.27), peak linear acceleration (g) (r = −0.25), peak rotational acceleration (rads/s2) (r = −0.27), and sum HITsp (r = −0.22).
Statistically significant individual predictor was peak linear acceleration (r = −0.19).
