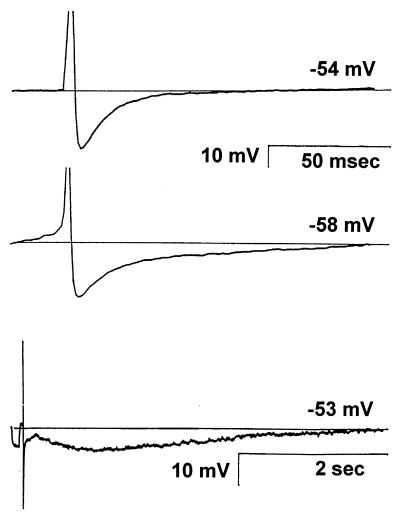
Figure 1.
A single AP can evoke three types of AHP in nodose neurons. (Top) A neuron with a single-component afterpotential lasting ≈30 ms. This AHP is designated AHPfast. All neurons have this short duration afterpotential. (Middle) Example of a neuron with two afterpotentials, an AHPfast followed by a longer lasting afterpotential (≈300 ms), the AHPmedium. In approximately half of the neurons, the AHPmedium is Ca2+-dependent. (Bottom) In a subset of C fiber type nodose neurons, a slowly developing (hundreds of ms) and long-lasting (2–15 s) afterpotential is observed. This slow afterpotential (AHPslow) is always Ca2+-dependent. Intracellular recordings were obtained at room temperature from adult neurons isolated from rabbit nodose ganglia. The values near the horizontal lines are resting membrane potentials. The calibration in the Top also applies to the Middle. Similar results have been recorded in guinea pig and ferret nodose neurons.