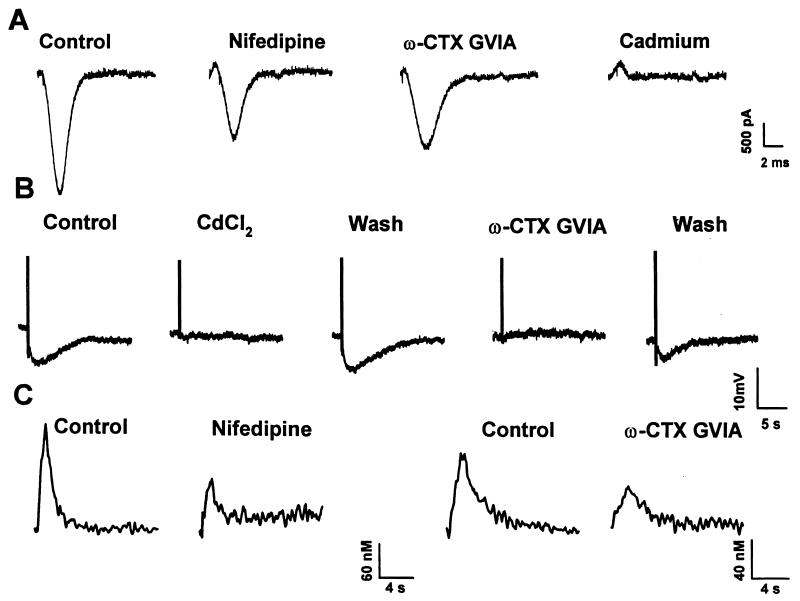
Figure 9.
Effects of VDCC antagonists on AP-induced calcium currents, AHPslow and AP-induced Ca2+ transients. (A) Inward calcium currents recorded in isolated nodose neurons evoked by a prerecorded AP waveform from a holding potential of −60 mV. From Left to Right, control inward current in the presence of 2 mM [Ca2+]o and in the presence of 10 μM nifedipine. After reestablishing control conditions, the neuron was exposed to 1 μM ω-conotoxin-GVIA. The effects of 500 μM cadmium were recorded in another neuron; the control current for this cell was similar to the first trace. (B) AHPslow evoked by a train of four APs (10 Hz) recorded in another nodose neuron. From Left to Right, AHPslow evoked in control conditions, in the presence of 100 μM CdCl2, after washout, in the presence of 500 nM ω-conotoxin-GVIA, and after washout. (C) AP-induced Ca2+ transients recorded in two nodose neurons. From Left to Right, Ca2+ transients evoked by a train of eight APs in normal Locke solution, and in Locke solution containing 10 μM nifedipine. In another neuron, 1 μM ω-conotoxin-GVIA reduced the Ca2+ transient ≈50% (see Table 4). APs were evoked by 2.5-ms, 10-Hz depolarizing current pulses.