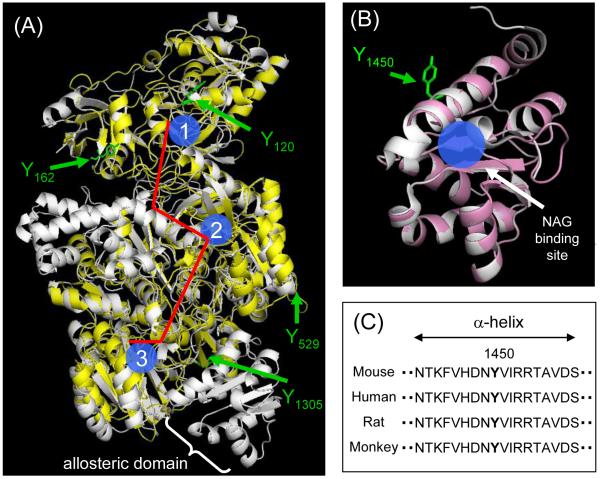
Figure 4.
Homology modeling of mouse CPS1. (A) The superimposed image of the created model of mouse CPS1 (yellow) with the template structure for the E. Coli CPS (white, PDB file: 1JDB). Three active sites are shown in blue (1: glutamine binding site, 2: bicarbonate binding site, 3: carbamoyl phosphate binding site) and the molecular tunnel is shown in red. (B) The superimposed image of the created model of the mouse NAG binding domain (pink) with the template structure for the human NAG binding domain (white, PBD file: 2YVQ). (C) The sequences (residues 1442 - 1459) in NAG binding domain of CPS1s from mouse (Mus musculus), human (Homo sapiens), rat (Rattus norvegicus) and monkey (Macaca mulatta), were obtained from the NCBI protein database.