Figure 2.
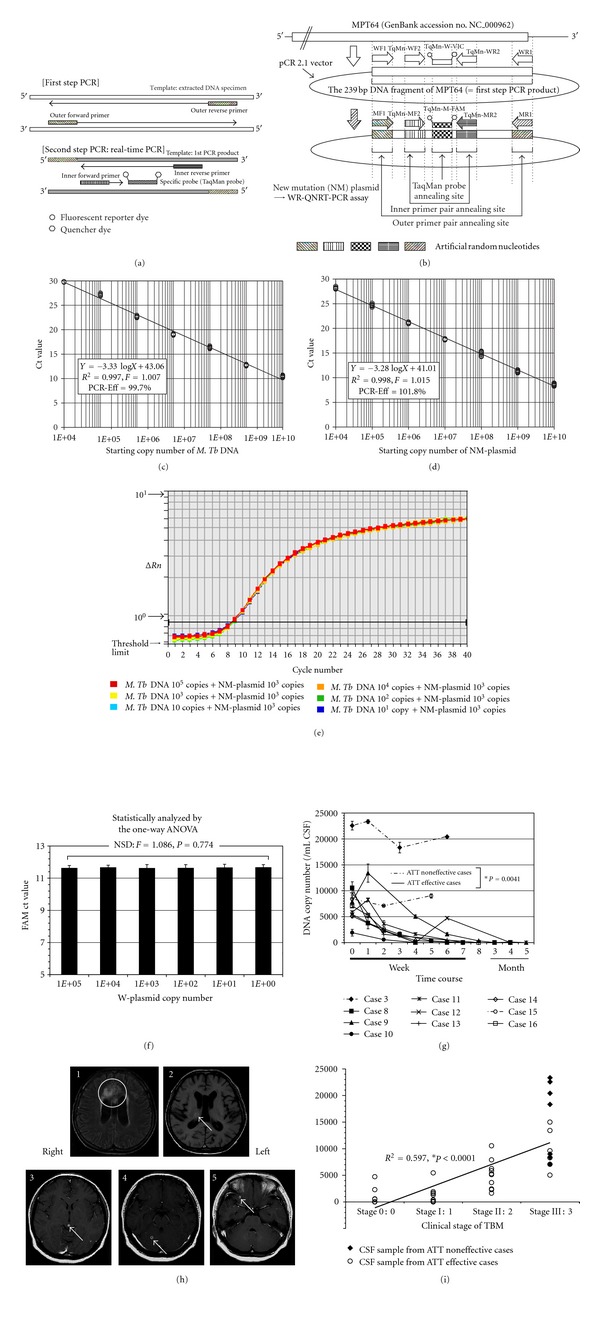
The principle of wide-range (WR) quantitative nested real-time (QNRT) PCR assay and its results. (a) A schema indicating the principle of WR-QNRT-PCR assay. (b) A schema of wild (W) and new mutation (NM) plasmids NM-plasmid was developed for use as a new internal control. (c) The specific standard curve to detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.Tb) DNA or W-plasmid quantitatively. (d) The specific standard curve to detect the NM-plasmid as a new internal control quantitatively. (e) Amplification curves for 103 copies of NM-plasmids as a new internal control. (f) One-way ANOVA against Ct values for 103 copies of NM-plasmid. (g) The progress of M.Tb DNA copy numbers calculated by the WR-QNRT-PCR assay during clinical time course in 10 suspected tuberculous meningitis (TBM) patients (cases 3 and 8–16). Statistical comparison between the cases in which anti-tuberculosis treatment (ATT) was effective (cases 8–14 and 16) and those in which it was not effective (cases 3 and 15) was carried out by repeated-measure ANOVA. (h) Cranial MRI findings for cases 11 and 12 on admission. 1, 2: Cranial MRI findings for case 11. 1: FLAIR image (TR 9000/TE 110). High-intensity lesions of cerebral infarction (circle), which were probably caused by tuberculous vasculitis, are noted on both sides of the frontal lobe. 2: T1-WI (TR 500/TE 17). A cranial tuberculoma was noted in the right thalamus. 3, 4, 5: Cranial MRI findings (Gd T1-WI: TR 400/TE 15) for case 12. Multiple cranial tuberculomas with marked Gd enhancement (arrows) were noted (3: midbrain, 4: right cerebellum, 5: right temporal lobe). (i) Result of simple regression analysis between M.Tb DNA copy number (y axis) and clinical stage of TBM (x axis).
