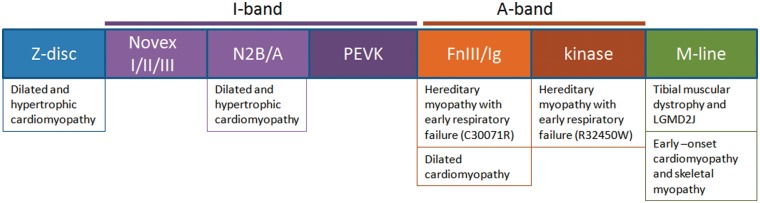
Figure 11.
Schematic diagram of the various domains of TTN (not drawn to scale), represented from N-terminus to C-terminus, and described based on their location within the sarcomere. There is some domain specificity for the observed phenotypes. Cardiomyopathy occurs from a broad range of mutations, although those in the N2B and A-band domains are most common (Herman et al., 2012). Mutations causing late-onset autosomal dominant myopathies are within the A-band, kinase region and M-line: tibial muscular dystrophy is caused by mutations in the M-line, and hereditary myopathy with early respiratory failure is now demonstrated to be caused by A-band or kinase mutations. The novex and N2B regions contain isoform-specific sequences (mainly for cardiac muscle). PEVK is the region characterized by repeats of amino acids PEVK. The A-band contains repetitive fibronectin III (FnIII) and immunoglobulin-like (Ig) elements (Gregorio et al., 1999; Bang et al., 2001; Freiburg et al., 2000; Krüger et al., 2009).