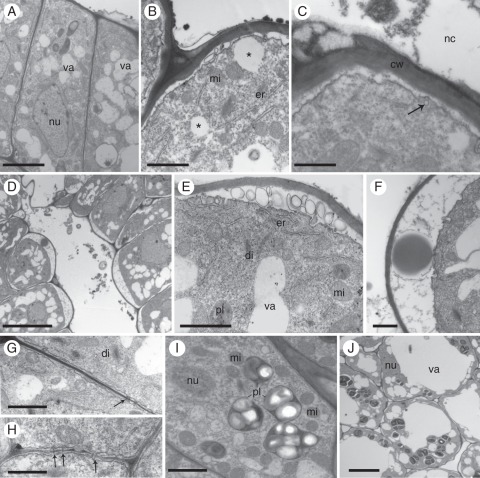
Fig. 3.
Septal nectary ultrastructure of Ananas ananassoides. (A) Epithelial cells. nu, nucleus; va, vacuole. Note an electron-opaque layer, probably remnants of secretion, on the surface of the outer periclinal wall. Scale bar = 5 µm. (B) Part of two epithelial cells showing undulating plasma membrane, lipophilic drops (*), mitochondria (mi) and endoplasmic reticulum (er). Scale bar = 1 µm. (C) Translucent vesicles (arrow) near the plasma membrane. Note the absence of cuticle. Scale bar = 0·5 µm. (D) Part of a secreting nectary showing epithelial cells with ample periplasmatic space in their apical pole; note secretion residues in the channel. Scale bar = 10 µm. (E) Part of an epithelial cell with endoplasmic reticulum (er), dictyosome (di), mitochondria (mi), plastid (pl) and vacuoles (va). Note lamellar bodies in the periplasmatic space. Scale bar = 1 µm. (F) Part of an epithelial cell with flocculated material and a large lipophilic drop in the periplasmatic space. Scale bar = 0·7 µm. (G) Plasmodesmata (arrows) in the anticlinal walls of epithelial cells. Scale bar = 1 µm. (H) Plasmodesmata (arrows) in the inner periclinal walls of epithelial cells. Scale bar = 1 µm. (I) Part of an epithelial cell with nucleus (nu), plastids (pl) packed with prominent starch grains, and mitochondria (mi). Scale bar = 1 µm. (J) Nectary parenchyma cells showing nucleus (nu), reduced cytoplasm, plastids and one well-developed central vacuole (va). Scale bar = 7 µm.