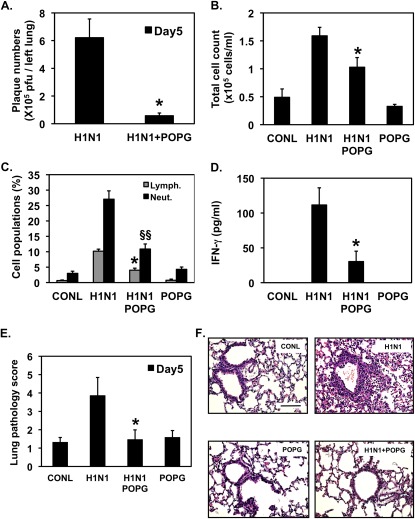
Figure 7.
POPG inhibits H1N1-PR8-IAV infection and inflammation in vivo and suppresses the histopathology elicited by the virus. BALB/c mice were infected with 80 pfu H1N1-PR8 (H1N1) by intranasal inoculation in either the absence or presence of 3 mg of POPG, as indicated. Sham (CONL) and lipid-only treatments (POPG) were also performed. After 5 days of infection, the animals were killed. (A) Amount of virus present in the left lung was quantified using plaque assays. *P < 0.01. (B) Lavage fluid collected from animals was used to quantify total cells recovered from the bronchoalveolar compartment. *P < 0.02. (C) Cytospin preparations were used to quantify the percentage of lymphocytes (Lymph.) and neutrophils (Neut.) present in the lavage fluid. *P < 0.01, §§P < 0.001. (D) The production of IFN-γ was measured in cell-free lavage fluid by ELISA. *P < 0.01. Each group contains four to six animals per individual experiment. (E) Paraffin sections (4 μm) were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, analyzed by light microscopy, and assigned a histopathology score. *P < 0.05. (F) Representative micrographs from the experiment. Values shown in A–E are means (±SE) for three independent experiments. Scale bar, 200 μm.