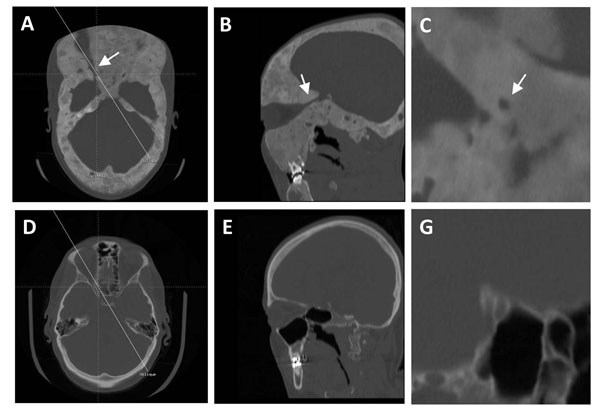
Figure 9.
Fibrous dysplasia encasing the optic nerve compared to a normal optic canal. A-C) A patient with extensive fibrous dysplasia (FD). The arrow indicates the optic canal. D-G) CT of a normal and uninvolved optic canal. Several CT slices through the optic canal are shown: A&D) axial, B&E) oblique, and C&G) coronal. A case-control study by Lee et al [13] demonstrated that statistically significant narrowing of the optic canal by FD did not result in vision loss. Thus, observation with regular ophthalmologic examinations in patients with asymptomatic encasement was a reasonable treatment option and optic nerve decompression was not warranted. Adapted from reference [13]