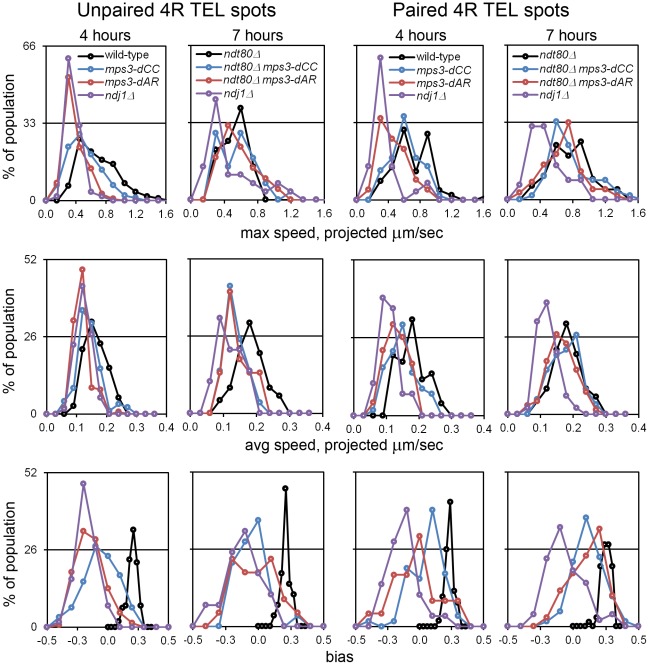
Figure 5. RPMs in the mps3-dAR and mps3-dCC mutants are intermediate between ndj1Δ and wild-type early in prophase and approach wild-type levels following pairing when prophase exit is blocked.
Histograms are shown to display the ranges and changes in RPMs with time by measures of maximum speed, average speed and bias. All measurements are for GFP-tagged spots adjacent to the 4R telomere and are accumulated separately for nuclei where there are 2 spots (unpaired, left columns) or 1 spot (paired, right columns). All populations are in early to middle meiotic prophase at 4 hours. To compare with the later 7 hour time-point of ndj1Δ, when many cells in the other strains would already be undergoing the meiotic divisions, ndt80Δ is added to the wild-type, mps3-dCC and msp3-dAR backgrounds to hold the strains in meiotic prophase and allow the development of the fastest possible RPMs. Note that the “bias” measure, the average of the cosines of the angles made between successive movements, is unitless. Statistical analyses of median values from t4 are in the legend to Table 1. Strains used: wild-type (MDY1560XMDY1567), mps3-dCC (MDY2580XMDY2759), mps3-dAR (MDY2523XMDY2756), ndj1Δ (MDY2294XMDY1560), ndt80Δ (MDY2984XMDY3021), ndt80Δ mps3-dCC (MDY3020XMDY3022), ndt80Δ mps3-dAR (MDY3047XMDY3049).