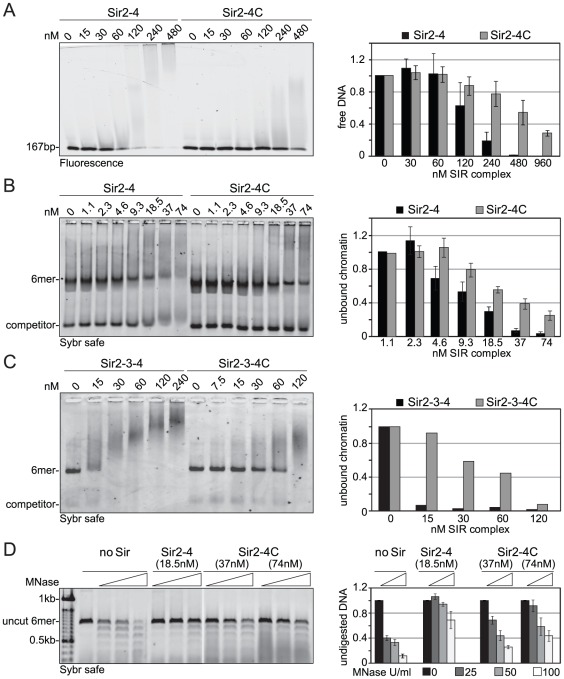
Figure 5. Sir4C has reduced affinity for DNA and chromatin and protects linker DNA less from MNase attack.
A) Increasing amounts of Sir2–Sir4 or Sir2–Sir4C complexes were titrated into a fixed amount of 167 bp 601-Widom Cy5-labeled DNA. Samples were separated by native agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized by Cy5 fluorescence. Binding in three independent experiments was quantified by measuring the disappearance of the unbound DNA and normalized to input; data represent mean value ± s.e.m. B) Sir2–Sir4 and Sir2–Sir4C complexes were titrated into constant amounts of 6 mer arrays of unmodified nucleosomes. Samples were analyzed as (A); chromatin was visualized by SybrSafe staining. C) Sir2–Sir3–Sir4 and Sir2–Sir3–Sir4C complexes were titrated into constant amounts of 6 mer arrays of unmodified nucleosomes as in (B), with only one experiment analyzed. D) Indicated concentrations of Sir2–Sir4 or Sir2–Sir4C were bound to chromatin as in (B) and incubated with increasing amounts of MNase for 10 min on ice prior to deproteinization. DNA was analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis and SybrSafe staining. The amount of full length 6 mer DNA was quantified to monitor degree of digestion. Data from at least three experiments are represented as mean value ± s.e.m.