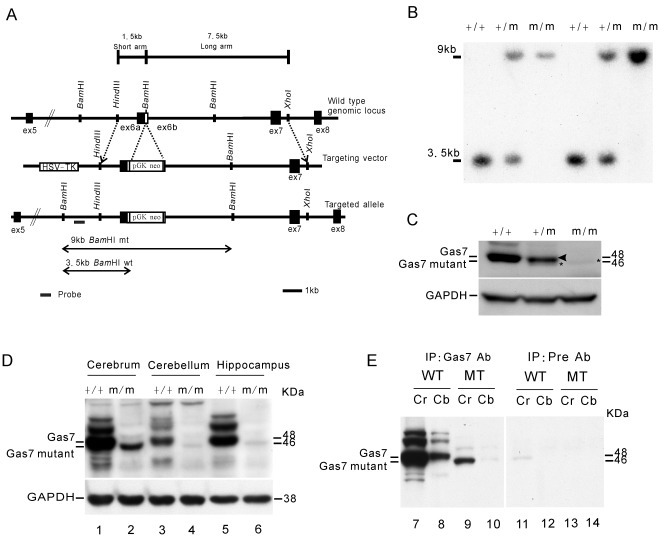
Figure 1. Disruption of gas7 gene and confirmation of Gas7 mutant protein expression.
(A) Maps of the Gas7 wild-type (+/+) and mutant (m/m) alleles. The gas7 gene targeting vector contained a neo cassette inserted into the unique BamHI site in exon 6 b. (B) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from gas7 +/+, gas7 +/m or gas7 m/m mice. Genomic DNA samples prepared from mouse tail were digested by BamHI and hybridized with a probe specific to the region between exon 5 and 6 of the Gas7 gene (bar) to distinguish the wild-type alleles from mutants. The band at 3.5 kb indicates the wild-type allele harboring the BamHI site. The 9 kb band represents the mutant allele, which was resistant to BamHI digestion. (C) Expression of Gas7 was examined in brain lysates from gas7 +/+, gas7 +/m or gas7 m/m mice. Gas7-deficient mice generated a mutant protein (asterisk) smaller in size than the wild-type Gas7 (arrowhead). (D) Expression of Gas7 and Gas7 mutant were examined in three brain regions including cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and hippocampus of wild-type and deficient mice. (E) Gas7 mutant expression in the cerebrum and cerebellum of the Gas7-deficient mice was confirmed by IP-Western using anti-Gas7 antibody. Gas7 mutant protein was not detected by pre-immune antibody in the cerebrum or cerebellum of the Gas7-deficient mice.