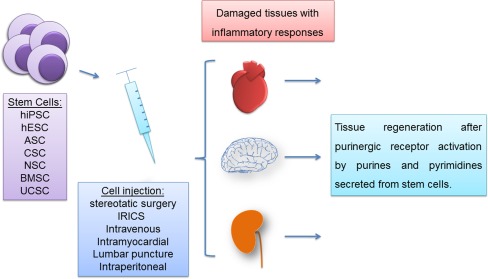
Fig. 1.
Therapeutic potential of stem cells and supposed effects of purinergic signaling. Stem cells of diverse origins, such as from adipose, cardiac, and neural tissues can restore and regenerate damaged tissues by secreting paracrine factors including purines and pyrimidines. ATP and adenosine interfere with tissue reactions following transplantation of stem cells of various origins in different ways. (1) Nucleotides modulate the immune response and thereby reduce inflammation processes and the risk of transplant rejection and cell death. (2) Purines and pyrimidines promote proliferation and differentiation of transplanted and endogenous stem cells by providing adequate stem cell niches. (3) Purines and pyrimidines promote migration of endogenous stem cells to the site of injury and increase engraftment rates. Stem cell types with therapeutic applications are human induced-pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC), human embryonic stem cells (hESC), adipose stem cells (ASC), cardiac stem cells (CSC), neural stem cells (NSC), bone marrow stem cells (BMSC), and umbilical cord stem cells (UCSC) which are transplanted by using stereotaxic surgery (SS), intracoronary retrograde infusion through coronary sinus (IRICS) or intravenous, intramyocardial, or intraperitoneal injection or lumbar puncture