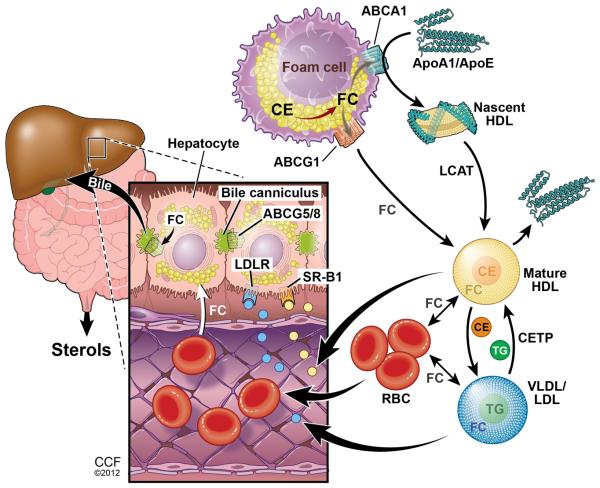
Figure 5.
Working model for the role of RBCs in RCT. Interstitial apoE, apoAI, HDL, and LDL can accept or exchange free cholesterol from foam cells and enter the blood stream. Lipoprotein free cholesterol can then be transferred to RBC plasma membranes. RBCs transit to the liver where they can donate free cholesterol directly to sinusoidal endothelial cells that are in contact with hepatocyte projections, or can deliver cholesterol to hepatocytes indirectly through cholesterol transfer to lipoproteins that can enter the space of Disse. Illustration by David Schumick, BS, CMI. Reprinted with the permission of the Cleveland Clinic Center for Medical Art & Photography © 2012. All Rights Reserved.