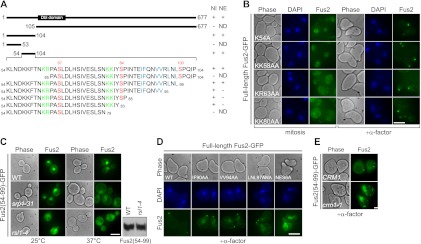
Figure 1.
Identification and characterization of Fus2p NLS and NES. (A) Schematic representation and summary of the functional sequences for Fus2p nuclear import (NI) and nuclear export (NE). (ND) Not determined. Essential sequences for nuclear import and export are highlighted in green and blue, respectively. Phosphorylation residues Ser 67, Ser 84, and Ser 100 are highlighted in red. A putative Dbl Rho-GEF domain is present at residues 116–321. (B) Fus2p point mutants (pMR6186, pMR6187, pMR6188, and pMR6189) were expressed in fus2Δ (MY10174) under the GAL1 promoter for 3 h (left), after which glucose and α-factor were added for 2 h (right). (C) Fus2p54–99 (pMR6159) was expressed under the GAL1 promoter in wild type (BY4741), srp1-31 (MY6457), and rsl1-4 (MY12131) for 30 min at 25°C; cells were then maintained at 25°C or shifted for 1 h to 37°C. Fus2p expression in rsl1-4 cells was shown by anti-GFP immunoblot. (D) Fus2p point mutants (pMR5469, pMR6192, pMR6191, pMR6190, and pMR6193) were expressed in fus2Δ (MY10174) under the GAL1 promoter for 3 h, after which glucose and α-factor were added for 2 h. (E) CRM1 (MY10239) and crm1-1 (MY10240) cells were arrested with α-factor for 90 min at 25°C, then cells were shifted to 37°C, and Fus2p54–99 (pMR6159) was expressed from the GAL1 promoter for 2 h. (B–E) Bar, 5 μm. (B,D) Cells were fixed and stained with DAPI. (C,E) GFP fluorescence was observed in living cells.