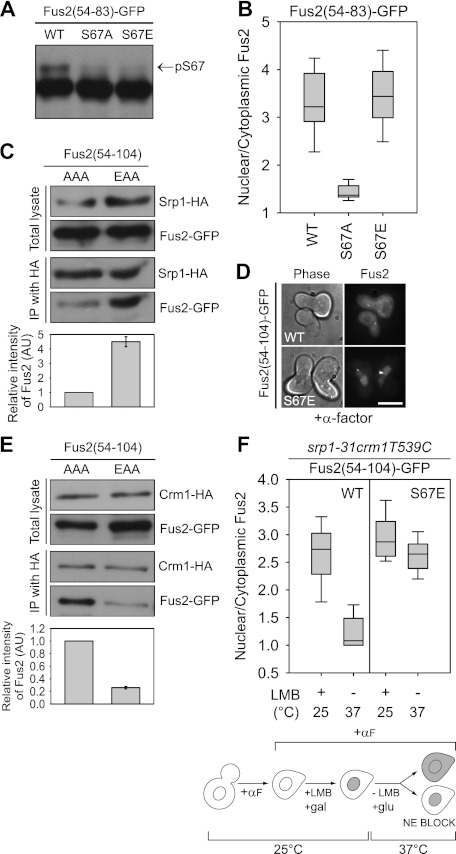
Figure 3.
The role of S67 phosphorylation in Fus2p transport. (A,B) Fus2p54–83 mutants (pMR6152, pMR6153, and pMR6154) were expressed in fus2Δ (MY10174) under the GAL1 promoter for 90 min. (A) Samples were run on 50 μM Phos-tag gels. The arrow indicates the S67 phosphorylated species. (B) GFP fluorescence was observed in living cells and quantified as described in Figure 2D. (C,E) Fus2p54–104 mutants (pMR6170 and pMR6173) were expressed in SRP1-3HA (MY12172) or CRM1-3HA (MY12170) cells under the GAL1 promoter for 90 min, and Srp1p or Crm1p was precipitated with anti-HA as described in the Materials and Methods. The intensity of copurified Fus2p was normalized by purified Srp1p or Crm1p and expressed relative to AAA. Error bars represent the means ± SEM of two independent experiments. AAA and EAA refer to residues 67, 84, and 100. (D) The indicated plasmids (pMR6009 and pMR6168) were expressed in fus2Δ (MY10174) under the GAL1 promoter for 90 min, after which glucose and α-factor were added for 2 h. GFP fluorescence was observed in living cells. Bar, 5 μm. (F) srp1-31 crm1T539C cells (MY12398) harboring the indicated plasmids (pMR6009 and pMR6168) were arrested with α-factor for 90 min, then galactose and 100 ng/mL LMB were added for 90 min at 25°C. After washing out the inhibitor, cells were incubated in glucose-containing and LMB-free medium for 90 min at 37°C. GFP fluorescence was observed in living cells and quantified as described in Figure 2D. (NE) Nuclear exit.