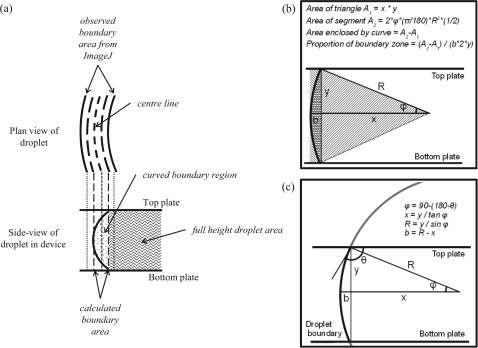
Figure 3.
(a) Schematic of both the plan and side-view of a droplet. The observed boundary area is divided by two to find the area inside the centre line. Half the calculated boundary area is then subtracted to find the area for which the droplet is full-height (the inner droplet area). This is multiplied by the spacer thickness to get the volume of the full-height section. The volume of the curved boundary region is then added. Calculations used to find (b) the cross-sectional area of the curved boundary region and (c) the predicted droplet boundary width.